The Versatile Applications of DES and Their Influence on Oxidoreductase-Mediated Transformations
- PMID: 31212686
- PMCID: PMC6600434
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24112190
The Versatile Applications of DES and Their Influence on Oxidoreductase-Mediated Transformations
Abstract
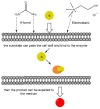
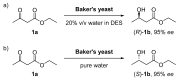
In the last decade, new types of solvents called deep eutectic solvents (DES) have been synthesized and commercialized. Among their main advantages, they can be eco-friendly and are easy to synthesize at different molar ratios depending on the desired solvent properties. This review aims to show the different uses of DES in some relevant biocatalytic redox reactions. Here we analyze oxidoreductase-mediated transformations that are performed in the presence of DES and compare them with the ones that avoided those solvents. DES were found to present advantages such as the increase in the product yield and enantiomeric excess in many reactions.
Keywords: asymmetric synthesis; biocatalysis; deep eutectic solvents; oxidoreductases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
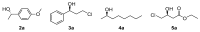

References
-
- Alonso D.A., Baeza A., Chinchilla R., Guillena G., Pastor I.M., Ramon D.J. Deep eutectic solvents: The organic reaction medium of the century. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016:612–632. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201501197. - DOI
-
- Tavares A.P.M., Rodríguez O., Macedo E.A. New generations of ionic liquids applied to enzymatic biocatalysis. In: Kadokawa J.-I., editor. Ionic Liquids. New Aspects for the Future. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2013. pp. 537–556. - DOI
-
- Walden P. Ueber die Molekulargrösse und Elektrische Leitfähigkeit einiger Geschmolzenen Salze. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 1914;8:405–422.
-
- Wilkes J.S., Zaworotko M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992:965–967. doi: 10.1039/c39920000965. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

