Non-Ionic Deep Eutectic Liquids: Acetamide-Urea Derived Room Temperature Solvents
- PMID: 31212745
- PMCID: PMC6627579
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122857
Non-Ionic Deep Eutectic Liquids: Acetamide-Urea Derived Room Temperature Solvents
Abstract
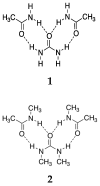
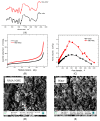
A family of non-ionic deep eutectic liquids has been developed based upon mixtures of solid N-alkyl derivatives of urea and acetamide that in some cases have melting points below room temperature. The eutectic behaviour and physical characteristics of a series of eleven eutectic mixtures are presented, along with a molecular dynamics study-supported hypothesis for the origin of the non-ideal mixing of these substances. Their use as solvents in applications ranging from natural product extraction to organic and polymer synthesis are demonstrated.
Keywords: acetamide–urea; deep-eutectic solvent; flickering cluster.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Atkins P. Physical Chemistry. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1980.
-
- Issac M.F. On the spontaneous crystallisation and the melting and freezing point curves of mixtures of two substances which form mixed crystals and posses a minimum or eutectic freezing point—Mixtures of azobenzene and benzylaniline. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A. 1910;84:344–369. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1910.0079. - DOI
-
- Zhang Y.Y., Ji X.Y., Lu X.H. Choline-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 separation: Review and thermodynamic analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018;97:436–455. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.08.007. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

