Overexpression of a Metallothionein 2A Gene from Date Palm Confers Abiotic Stress Tolerance to Yeast and Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 31212812
- PMCID: PMC6627811
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122871
Overexpression of a Metallothionein 2A Gene from Date Palm Confers Abiotic Stress Tolerance to Yeast and Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
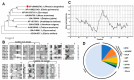
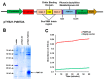
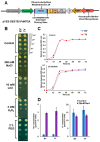
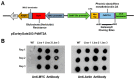
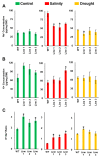
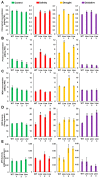
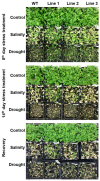
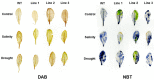
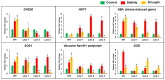
Although the date palm tree is an extremophile with tolerance to drought and certain levels of salinity, the damage caused by extreme salt concentrations in the soil, has created a need to explore stress-responsive traits and decode their mechanisms. Metallothioneins (MTs) are low-molecular-weight cysteine-rich proteins that are known to play a role in decreasing oxidative damage during abiotic stress conditions. Our previous study identified date palm metallothionein 2A (PdMT2A) as a salt-responsive gene, which has been functionally characterized in yeast and Arabidopsis in this study. The recombinant PdMT2A protein produced in Escherichia coli showed high reactivity against the substrate 5'-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB), implying that the protein has the property of scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS). Heterologous overexpression of PdMT2A in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) conferred tolerance to drought, salinity and oxidative stresses. The PdMT2A gene was also overexpressed in Arabidopsis, to assess its stress protective function in planta. Compared to the wild-type control, the transgenic plants accumulated less Na+ and maintained a high K+/Na+ ratio, which could be attributed to the regulatory role of the transgene on transporters such as HKT, as demonstrated by qPCR assay. In addition, transgenic lines exhibited higher chlorophyll content, higher superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and improved scavenging ability for reactive oxygen species (ROS), coupled with a better survival rate during salt stress conditions. Similarly, the transgenic plants also displayed better drought and oxidative stress tolerance. Collectively, both in vitro and in planta studies revealed a role for PdMT2A in salt, drought, and oxidative stress tolerance.
Keywords: abiotic stress; date palm; drought; functional characterization; metallothionein; salinity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Characterization of Date Palm Aquaporin Gene PdPIP1;2 Confers Drought and Salinity Tolerance to Yeast and Arabidopsis.Genes (Basel). 2019 May 22;10(5):390. doi: 10.3390/genes10050390. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31121945 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of a Date Palm Vascular Highway 1-Interacting Kinase (PdVIK) Under Abiotic Stresses.Genes (Basel). 2020 May 19;11(5):568. doi: 10.3390/genes11050568. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32438658 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous expression of the Leymus chinensis metallothionein gene LcMT3 confers enhanced tolerance to salt stress in Escherichia coli, yeast, and Arabidopsis thaliana.J Plant Physiol. 2023 Aug;287:154022. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2023.154022. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37301036
-
Abiotic stress-induced anthocyanins in plants: Their role in tolerance to abiotic stresses.Physiol Plant. 2021 Jul;172(3):1711-1723. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13373. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Physiol Plant. 2021. PMID: 33605458 Review.
-
Molecular priming as an approach to induce tolerance against abiotic and oxidative stresses in crop plants.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 May-Jun;40:107503. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107503. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 31901371 Review.
Cited by
-
Metallothionein: A Comprehensive Review of Its Classification, Structure, Biological Functions, and Applications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 9;13(7):825. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070825. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in physio-biochemical parameters and expression of metallothioneins in Avena sativa L. in response to drought.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 12;13(1):2486. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29394-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36775830 Free PMC article.
-
Silicon and Gibberellins: Synergistic Function in Harnessing ABA Signaling and Heat Stress Tolerance in Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.).Plants (Basel). 2020 May 13;9(5):620. doi: 10.3390/plants9050620. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32413955 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothionein-2A Protects Cardiomyocytes from Hypoxia/reper-Fusion through Inhibiting p38.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Mar;81(1):69-75. doi: 10.1007/s12013-022-01118-9. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 36445616
-
Recent advances in date palm genomics: A comprehensive review.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 13;13:959266. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.959266. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36176294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gill S.S., Anjum N.A., Gill R., Mahajan M., Tuteja N. Abiotic stress tolerance and sustainable agriculture: A functional genomics perspective. In: Pandey G.K., editor. Elucidation of Abiotic Stress Signaling in Plants: Functional Genomics Perspectives. Volume 2. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2015. pp. 439–472.
-
- Chao C.T., Krueger R.R. The date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.): Overview of biology, uses, and cultivation. HortScience. 2007;42:1077–1082. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.42.5.1077. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

