In Silico Transcriptomic Analysis of Wound-Healing-Associated Genes in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
- PMID: 31212858
- PMCID: PMC6631992
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina55060267
In Silico Transcriptomic Analysis of Wound-Healing-Associated Genes in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
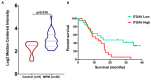
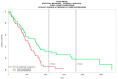
Background and objectives: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a devastating malignancy with poor prognosis. Reliable biomarkers for MPM diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis are needed. The aim of this study was to identify genes associated with wound healing processes whose expression could serve as a prognostic factor in MPM patients. Materials and Methods: We used data mining techniques and transcriptomic analysis so as to assess the differential transcriptional expression of wound-healing-associated genes in MPM. Moreover, we investigated the potential prognostic value as well as the functional enrichments of gene ontologies relative to microRNAs (miRNAs) of the significantly differentially expressed wound-healing-related genes in MPM. Results: Out of the 82 wound-healing-associated genes analyzed, 30 were found significantly deregulated in MPM. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that low ITGAV gene expression could serve as a prognostic factor favoring survival of MPM patients. Finally, gene ontology annotation enrichment analysis pointed to the members of the hsa-miR-143, hsa-miR-223, and the hsa-miR-29 miRNA family members as important regulators of the deregulated wound healing genes. Conclusions: 30 wound-healing-related genes were significantly deregulated in MPM, which are potential targets of hsa-miR-143, hsa-miR-223, and the hsa-miR-29 miRNA family members. Out of those genes, ITGAV gene expression was a prognostic factor of overall survival in MPM. Our results highlight the role of impaired tissue repair in MPM development and should be further validated experimentally.
Keywords: in silico; malignant pleural mesothelioma; miRNA; transcriptomics; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nasreen N., Mohammed K.A., Mubarak K.K., Baz M.A., Akindipe O.A., Fernandez-Bussy S., Antony V.B. Pleural mesothelial cell transformation into myofibroblasts and haptotactic migration in response to TGF-β1 in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009;297:L115–L124. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90587.2008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

