Sit4 and PP2A Dephosphorylate Nitrogen Catabolite Repression-Sensitive Gln3 When TorC1 Is Up- as Well as Downregulated
- PMID: 31213504
- PMCID: PMC6707456
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.119.302371
Sit4 and PP2A Dephosphorylate Nitrogen Catabolite Repression-Sensitive Gln3 When TorC1 Is Up- as Well as Downregulated
Abstract
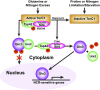
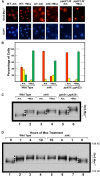
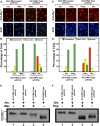
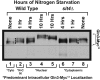
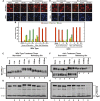
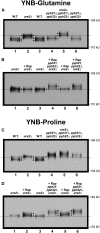
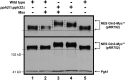
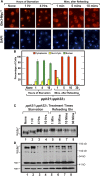
Saccharomyces cerevisiae lives in boom and bust nutritional environments. Sophisticated regulatory systems have evolved to rapidly cope with these changes while preserving intracellular homeostasis. Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (TorC1), is a serine/threonine kinase complex and a principle nitrogen-responsive regulator. TorC1 is activated by excess nitrogen and downregulated by limiting nitrogen. Two of TorC1's many downstream targets are Gln3 and Gat1-GATA-family transcription activators-whose localization and function are Nitrogen Catabolite Repression- (NCR-) sensitive. In nitrogen replete environments, TorC1 is activated, thereby inhibiting the PTap42-Sit4 and PTap42-PP2A (Pph21/Pph22-Tpd3, Pph21,22-Rts1/Cdc55) phosphatase complexes. Gln3 is phosphorylated, sequestered in the cytoplasm and NCR-sensitive transcription repressed. In nitrogen-limiting conditions, TorC1 is downregulated and PTap42-Sit4 and PTap42-PP2A are active. They dephosphorylate Gln3, which dissociates from Ure2, relocates to the nucleus, and activates transcription. A paradoxical observation, however, led us to suspect that Gln3 control was more complex than appreciated, i.e., Sit4 dephosphorylates Gln3 more in excess than in limiting nitrogen conditions. This paradox motivated us to reinvestigate the roles of these phosphatases in Gln3 regulation. We discovered that: (i) Sit4 and PP2A actively function both in conditions where TorC1 is activated as well as down-regulated; (ii) nuclear Gln3 is more highly phosphorylated than when it is sequestered in the cytoplasm; (iii) in nitrogen-replete conditions, Gln3 relocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where it is dephosphorylated by Sit4 and PP2A; and (iv) in nitrogen excess and limiting conditions, Sit4, PP2A, and Ure2 are all required to maintain cytoplasmic Gln3 in its dephosphorylated form.
Keywords: Gln3; PP2A; Sit4; TorC1; Ure2; nitrogen catabolite repression; rapamycin.
Copyright © 2019 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct phosphatase requirements and GATA factor responses to nitrogen catabolite repression and rapamycin treatment in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 4;285(23):17880-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.085712. Epub 2010 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20378536 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin-induced Gln3 dephosphorylation is insufficient for nuclear localization: Sit4 and PP2A phosphatases are regulated and function differently.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 23;284(4):2522-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806162200. Epub 2008 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19015262 Free PMC article.
-
General Amino Acid Control and 14-3-3 Proteins Bmh1/2 Are Required for Nitrogen Catabolite Repression-Sensitive Regulation of Gln3 and Gat1 Localization.Genetics. 2017 Feb;205(2):633-655. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.195800. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28007891 Free PMC article.
-
Transmitting the signal of excess nitrogen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from the Tor proteins to the GATA factors: connecting the dots.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002 Aug;26(3):223-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2002.tb00612.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12165425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A on track for nutrient-induced signalling in yeast.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Feb;43(4):835-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02786.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11929536 Review.
Cited by
-
Disordered sequences of transcription factors regulate genomic binding by integrating diverse sequence grammars and interaction types.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 27;52(15):8763-8777. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae521. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38908024 Free PMC article.
-
TorC1 and nitrogen catabolite repression control of integrated GABA shunt and retrograde pathway gene expression.Yeast. 2023 Aug;40(8):318-332. doi: 10.1002/yea.3849. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Yeast. 2023. PMID: 36960709 Free PMC article.
-
N- and C-terminal Gln3-Tor1 interaction sites: one acting negatively and the other positively to regulate nuclear Gln3 localization.Genetics. 2021 Apr 15;217(4):iyab017. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab017. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33857304 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of abolishing Whi2 on the proteome and nitrogen catabolite repression-sensitive protein production.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Mar 4;12(3):jkab432. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab432. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35100365 Free PMC article.
-
TORC1 Signaling Controls the Stability and Function of α-Arrestins Aly1 and Aly2.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 31;12(4):533. doi: 10.3390/biom12040533. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454122 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

