Association between prefrontal glutamine levels and neuroticism determined using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- PMID: 31213596
- PMCID: PMC6581909
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-019-0500-z
Association between prefrontal glutamine levels and neuroticism determined using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Abstract
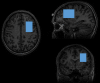
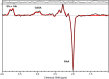
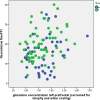
There is growing evidence for GABA and glutamate-glutamine dysfunction in the pathogenesis of mood and anxiety disorders. It is important to study this pathology in the early phases of the illness in order to develop new approaches to secondary prevention. New magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) measures allow determining glutamine, the principal metabolite of synaptic glutamate that is directly related to glutamate levels in the synaptic cleft, as well as glutamate and GABA. In contrast to previous investigations, this study used community-based recruitment methods and a combined categorical and dimensional approach to psychopathology. In the study protocol, neuroticism was defined as the primary outcome. Neuroticism shares a large proportion of its genetic variance with mood and anxiety disorders. We examined young adult participants recruited from the general population in a cross-sectional study using 3-T 1H-MRS with one voxel in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC). The total sample of N = 110 (61 females) included 18 individuals suffering from MDD and 19 individuals suffering from DSM-IV anxiety disorders. We found that glutamine and glutamine-to-glutamate ratio were correlated with neuroticism in the whole sample (r = 0.263, p = 0.005, and n = 110; respectively, r = 0.252, p = 0.008, and n = 110), even when controlling for depression and anxiety disorder diagnoses (for glutamine: beta = 0.220, p = 0.047, and n = 110). Glutamate and GABA were not significantly correlated with neuroticism (r = 0.087, p = 0.365, and n = 110; r = -0.044, p = 0.645, and n = 110). Lack of self-confidence and emotional instability were the clinical correlates of glutamate-glutamine dysfunction. In conclusion, this study suggests that prefrontal glutamine is increased in early phases of mood and anxiety disorders. Further understanding of glutamate-glutamine dysfunction in stress-related disorders may lead to new therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat these disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures