Neuroergonomics Applications of Electroencephalography in Physical Activities: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 31214002
- PMCID: PMC6558147
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00182
Neuroergonomics Applications of Electroencephalography in Physical Activities: A Systematic Review
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Neuroergonomics Applications of Electroencephalography in Physical Activities: A Systematic Review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Aug 13;13:277. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00277. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31456673 Free PMC article.
Abstract
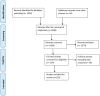
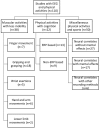
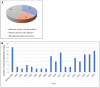
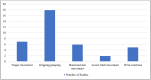
Recent years have seen increased interest in neuroergonomics, which investigates the brain activities of people engaged in diverse physical and cognitive activities at work and in everyday life. The present work extends upon prior assessments of the state of this art. However, here we narrow our focus specifically to studies that use electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brain activity, correlates, and effects during physical activity. The review uses systematically selected, openly published works derived from a guided search through peer-reviewed journals and conference proceedings. Identified studies were then categorized by the type of physical activity and evaluated considering methodological and chronological aspects via statistical and content-based analyses. From the identified works (n = 110), a specific number (n = 38) focused on less mobile muscular activities, while an additional group (n = 22) featured both physical and cognitive tasks. The remainder (n = 50) investigated various physical exercises and sporting activities and thus were here identified as a miscellaneous grouping. Most of the physical activities were isometric exertions, moving parts of upper and lower limbs, or walking and cycling. These primary categories were sub-categorized based on movement patterns, the use of the event-related potentials (ERP) technique, the use of recording methods along with EEG and considering mental effects. Further information on subjects' gender, EEG recording devices, data processing, and artifact correction methods and citations was extracted. Due to the heterogeneous nature of the findings from various studies, statistical analyses were not performed. These were thus included in a descriptive fashion. Finally, contemporary research gaps were pointed out, and future research prospects to address those gaps were discussed.
Keywords: EEG; brain; ergonomics; human factors; neuroergonomics; physical activity; physical exercise; physical exertion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Applications of EEG indices for the quantification of human cognitive performance: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 4;15(12):e0242857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242857. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33275632 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroergonomics on the Go: An Evaluation of the Potential of Mobile EEG for Workplace Assessment and Design.Hum Factors. 2023 Feb;65(1):86-106. doi: 10.1177/00187208211007707. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Hum Factors. 2023. PMID: 33861182 Free PMC article.
-
Electroencephalography (EEG) Physiological Indices Reflecting Human Physical Performance: A Systematic Review Using Updated PRISMA.J Integr Neurosci. 2023 May 8;22(3):62. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2203062. J Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37258434
-
Corrigendum: Neuroergonomics Applications of Electroencephalography in Physical Activities: A Systematic Review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Aug 13;13:277. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00277. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31456673 Free PMC article.
-
EEG signatures of arm isometric exertions in preparation, planning and execution.Neuroimage. 2014 Apr 15;90:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.12.011. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24355482
Cited by
-
Modeling Brain Functional Connectivity Patterns during an Isometric Arm Force Exertion Task at Different Levels of Perceived Exertion: A Graph Theoretical Approach.Brain Sci. 2022 Nov 18;12(11):1575. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12111575. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36421899 Free PMC article.
-
New Directions in Exercise Prescription: Is There a Role for Brain-Derived Parameters Obtained by Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy?Brain Sci. 2020 Jun 3;10(6):342. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10060342. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 32503207 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of EEG indices for the quantification of human cognitive performance: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 4;15(12):e0242857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242857. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33275632 Free PMC article.
-
Using Electroencephalography (EEG) Power Responses to Investigate the Effects of Ambient Oxygen Content, Safety Shoe Type, and Lifting Frequency on the Worker's Activities.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 4;2020:7956037. doi: 10.1155/2020/7956037. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32337279 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroergonomics on the Go: An Evaluation of the Potential of Mobile EEG for Workplace Assessment and Design.Hum Factors. 2023 Feb;65(1):86-106. doi: 10.1177/00187208211007707. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Hum Factors. 2023. PMID: 33861182 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

