Impact of socio-demographic factors, lifestyle and health status on nutritional status among the elderly in Taiwan
- PMID: 31214290
- PMCID: PMC6548706
- DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.3.222
Impact of socio-demographic factors, lifestyle and health status on nutritional status among the elderly in Taiwan
Abstract
Background/objectives: Aging is an imperative problem for many countries in this century, and presents several challenges for the maintenance of good nutritional status. This study aims to assess the impact of socio-demographic factors, lifestyle and health status on the nutritional status among the elderly in Taiwan.
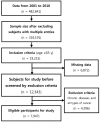
Subjects/methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out in Taiwan. Data were obtained from the Mei Jau Health Management Institution, which is a private health evaluation provider with multiple health screening centers in Taiwan and Asia. This study included 7947 adults aged 65 years or above. The data were extracted between 2001 to 2010. Nutritional status was assessed using anthropometric data, biochemical data and dietary intake information.
Results: Among the 7947 participants with mean age of 70.1 (SD = 4.5) years, 20.2%, 6.6%, 10.5% and 52.5% experienced underweight, protein malnutrition, anemia and inadequate dietary intake in the past month, respectively. Age was negatively correlated with body weight (r = -0.19, P = 0.02), body mass index (r = -0.41, P < 0.001), albumin level (r = -0.93, P < 0.001) and hemoglobin level (r = -0.30, P = 0.008). Age above 70 years, gender, unmarried status, retirement, lack of education, low family income, smoking, alcohol drinking, sleep duration of 6-8 hours, vegetarian diet, multiple medications, comorbidity and dysphagia were positively associated with malnutrition in older adults.
Conclusions: Underweight and inadequate dietary intake are prevalent among the elderly in Taiwan. Vegetarian diet, multiple medications, comorbidity, dysphagia and lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol drinking and sleep duration of 6-8 hours are risk factors for undernutrition in older adults.
Keywords: Taiwan; Undernutrition; diet; elderly; lifestyle.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Demographic, Socio-economic and Lifestyle Determinants of Under- and Over-nutrition among Bangladeshi Adult Population: Results from a Large Cross-Sectional Study.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2018 Dec;8(3-4):134-142. doi: 10.2991/j.jegh.2018.03.002. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2018. PMID: 30864754 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Dietary Pattern, Lifestyle, Anthropometric Status, and Anemia-Related Biomarkers among Adults: A Population-Based Study from 2001 to 2015.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 26;18(7):3438. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073438. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33810272 Free PMC article.
-
Undernutrition and obesity among elderly people living in two cities of developing countries: Prevalence and associated factors in the EDAC study.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2017 Oct;21:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2017. PMID: 30014868
-
Identifying the elderly at risk for malnutrition. The Mini Nutritional Assessment.Clin Geriatr Med. 2002 Nov;18(4):737-57. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0690(02)00059-9. Clin Geriatr Med. 2002. PMID: 12608501 Review.
-
Nutrition and socio-economic development in Southeast Asia.Proc Nutr Soc. 1992 May;51(1):93-104. doi: 10.1079/pns19920014. Proc Nutr Soc. 1992. PMID: 1508934 Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol Consumption among the Elderly Citizens in Hungary and Serbia-Comparative Assessment.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Feb 17;17(4):1289. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17041289. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32079338 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of malnutrition and associated factors among older adults from urban and rural residences of Metu district, Southwest Ethiopia.BMC Nutr. 2022 May 30;8(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40795-022-00532-9. BMC Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35637535 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional status and its associated factors among elderly people in Ilu Aba Bor Zone, Southwest Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2023 Jan 31;13(1):e067787. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067787. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 36720579 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of nutrition education intervention to improve dietary diversity practice and nutritional status of the older people: A cluster randomized controlled trial.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Sep 13;11(11):7383-7395. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3667. eCollection 2023 Nov. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37970381 Free PMC article.
-
A Logical Framework (MYGERYFS) for Hospital Foodservice to Prevent Malnutrition Among Geriatric Patients in Hospitals, Malaysia: Protocol for a Feasibility Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2023 Jan 31;12:e42496. doi: 10.2196/42496. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023. PMID: 36719732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Health statistics and information systems [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. [cited 2016 August 19]. Available from: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/survey/ageingdefnolder/en/
-
- World Health Organization; National Institutes of Health (US); National Institute on Aging (US) Global health and aging [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011. [cited 2016 August 19]. Available from: http://www.who.int/ageing/publications/global_health.pdf.
-
- Chen LK, Inoue H, Won CW, Lin CH, Lin KF, Tsay SF, Lin PF, Li SH. Challenges of urban aging in Taiwan: summary of urban aging forum. J Clin Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;4:97–101.
-
- Lu L. Aging and quality of life in Taiwan. J Altern Med Res. 2012;4:233–243.
-
- National Statistics (TW) Yearly statistics: population and housing [Internet] Taipei: National Statistics; 2016. [cited 2016 August 19]. Available from: http://eng.stat.gov.tw/lp.asp?ctNode=2265&CtUnit=1072&BaseDSD=36&mp=5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous