Theranostic Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles With Potential for Multimodal Imaging and Drug Delivery
- PMID: 31214583
- PMCID: PMC6558148
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00126
Theranostic Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles With Potential for Multimodal Imaging and Drug Delivery
Abstract
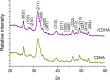
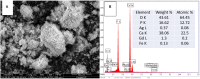
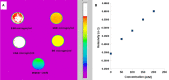
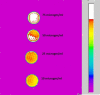
Calcium phosphate (CaP) bioceramics closely resemble the natural human bone, which is a main reason for their popularity as bone substitutes. However, this compositional similarity makes it difficult to distinguish CaPs, especially in particulate form, from native bone by imaging modalities such as X-ray radiography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to monitor the healing progress. External contrast agents can improve the imaging contrast of CaPs but can affect their physicochemical properties and can produce artifacts. In this work, we have attempted to improve the contrast of CaP nanoparticles via ion substitutions for multimodal imaging. Calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite (CDHA) nanoparticles with silver (Ag), gadolinium (Gd), and iron (Fe) substitution were prepared by a microwave-accelerated wet chemical process to improve the contrast in CT, T1 (spin-lattice), and T2 (spin-spin) MRI relaxation modes, respectively. Ag, Gd, and Fe were substituted at 0.25, 0.5, and 0.25 at.%, respectively. The ion-substituted CDHA (ICDHA) was found to be phase pure by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images showed that the ICDHA nanoparticles were platelet shaped and of 52 ± 2 nm length and 6 ± 1 nm width. The ICDHA showed high contrast in X-ray and CT compared to CDHA. The vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) studies showed the ICDHA to exhibit paramagnetic behavior compared to diamagnetic CDHA, which was further confirmed by improved contrast in T1 and T2 MRI mode. In addition, the in vitro tetracycline drug loading and release was studied to investigate the capability of these nanoparticles for antibiotic drug delivery. It was found that a burst release profile was observed for 24 h with 47-52% tetracycline drug release. The ICDHA nanoparticles also showed in vitro antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli due to Ag, which was further enhanced by antibiotic loading. In vitro biocompatibility studies showed that the triple-ion-substituted ICDHA nanoparticles were cytocompatible. Thus, the ion-substituted CDHA nanoparticles can have potential theranostic applications due to their multimodal image contrast, antibacterial activity, and drug delivery potential. Future work will be conducted with actual bone samples in vitro or in animal models.
Keywords: antibacterial; bone substitute; calcium phosphate nanoparticles; drug delivery; image contrast; ion substitution; multimodal imaging; theranostics.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Dual mode antibacterial activity of ion substituted calcium phosphate nanocarriers for bone infections.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 May 1;3:59. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00059. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25984512 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and bone-regenerative dual-drug-loaded calcium phosphate nanocarriers-in vitro and in vivo studies.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018 Oct;8(5):1066-1077. doi: 10.1007/s13346-018-0532-6. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29717475
-
Blood compatibility of iron-doped nanosize hydroxyapatite and its drug release.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012 Mar;4(3):1200-10. doi: 10.1021/am300140q. Epub 2012 Mar 5. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012. PMID: 22316071
-
Microwave accelerated synthesis of nanosized calcium deficient hydroxyapatite.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004 Dec;15(12):1279-84. doi: 10.1007/s10856-004-5735-3. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004. PMID: 15747179
-
Gadolinium-based layered double hydroxide and graphene oxide nano-carriers for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery.Chem Cent J. 2017 May 30;11(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13065-017-0275-3. Chem Cent J. 2017. PMID: 29086824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles Carrying NF-κB p65-Specific siRNA Alleviate Colitis in Mice by Attenuating NF-κB-Related Protein Expression and Pro-Inflammatory Cellular Mediator Secretion.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 15;14(2):419. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020419. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214151 Free PMC article.
-
Eu-Doped Citrate-Coated Carbonated Apatite Luminescent Nanoprobes for Drug Delivery.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jan 23;10(2):199. doi: 10.3390/nano10020199. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31979272 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Synthesis Conditions on Gadolinium-Substituted Tricalcium Phosphate Ceramics and Its Physicochemical, Biological, and Antibacterial Properties.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Mar 3;12(5):852. doi: 10.3390/nano12050852. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35269340 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional cell membranes-based nano-carriers for targeted therapies: a review of recent trends and future perspective.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2288797. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2288797. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 38069500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Nanohydroxyapatite in Medicine-A Narrative Review.Molecules. 2024 Nov 28;29(23):5628. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235628. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashokan A., Gowda G. S., Somasundaram V. H., Bhupathi A., Peethambaran R., Unni A. K. K., et al. . (2013). Multifunctional calcium phosphate nano-contrast agent for combined nuclear, magnetic and near-infrared in vivo imaging. Biomaterials 34, 7143–7157. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.05.077 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

