Effect of sevoflurane on systemic and cerebral circulation, cerebral autoregulation and CO2 reactivity
- PMID: 31215448
- PMCID: PMC6582518
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-019-0784-9
Effect of sevoflurane on systemic and cerebral circulation, cerebral autoregulation and CO2 reactivity
Abstract
Background: Sevoflurane is one of the most frequently used inhaled anesthetics for general anesthesia. Previously it has been reported that at clinically used doses of sevoflurane, cerebral vasoreactivity is maintained. However, there are no data how sevoflurane influences systemic and cerebral circulation in parallel. The aim of our study was to assess systemic and cerebral hemodynamic changes as well as cerebral CO2-reactivity during sevoflurane anesthesia.
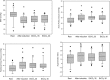
Methods: Twenty nine patients undergoing general anesthesia were enrolled. Anesthesia was maintained with 1 MAC sevoflurane in 40% oxygen. Ventilatory settings (respiratory rate and tidal volume) were adjusted to reach and maintain 40, 35 and 30 mmHg EtCO2 for 5 min respectively. At the end of each period, transcranial Doppler and hemodynamic parameters using applanation tonometry were recorded.
Results: Systemic mean arterial pressure significantly decreased during anesthetic induction and remained unchanged during the entire study period. Central aortic and peripherial pulse pressure and augmentation index as markers of arterial stiffness significantly increased during the anesthetic induction and remained stable at the time points when target CO2 levels were reached. Both cerebral autoregulation and cerebral CO2-reactivity was maintained at 1 MAC sevoflurane.
Discussion: Cerebral autoregulation and CO2-reactivity is preserved at 1 MAC sevoflurane. Cerebrovascular effects of anesthetic compounds have to be assessed together with systemic circulatory effects.
Trial registration: The study was registered at http://www.clinicaltrials.gov , identifier: NCT02054143, retrospectively registered. Date of registration: February 4, 2014.
Keywords: CO2-reactivity, applanation tonometry; Cerebral blood flow, cerebral autoregulation; Sevoflurane; Transcranial Doppler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The effect of propofol-sufentanil intravenous anesthesia on systemic and cerebral circulation, cerebral autoregulation and CO2 reactivity: a case series.Braz J Anesthesiol. 2021 Sep-Oct;71(5):558-564. doi: 10.1016/j.bjane.2021.04.002. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2021. PMID: 33901551 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dexmedetomidine on dynamic cerebral autoregulation and carbon dioxide reactivity during sevoflurane anesthesia in healthy patients.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2020 Aug;73(4):311-318. doi: 10.4097/kja.19246. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32209963 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dynamic cerebral autoregulation during sevoflurane anesthesia: a comparison with isoflurane.Anesth Analg. 1999 Feb;88(2):341-5. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199902000-00022. Anesth Analg. 1999. PMID: 9972753
-
Cerebral autoregulation and anesthesia.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2009 Oct;22(5):547-52. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e32833020be. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2009. PMID: 19620861 Review.
-
Do acute stroke patients develop hypocapnia? A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurol Sci. 2019 Jul 15;402:30-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2019.04.038. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31102829
Cited by
-
Impact of Intraoperative Fluctuations of Cardiac Output on Cerebrovascular Autoregulation: An Integrative Secondary Analysis of Individual-level Data.J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2024 Oct 1;36(4):334-340. doi: 10.1097/ANA.0000000000000944. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38011867 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of noradrenaline and phenylephrine on cerebral oxygen saturation during cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery.Exp Physiol. 2025 Jun;110(6):798-808. doi: 10.1113/EP092387. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Exp Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39853666 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risk of overestimating loss of cerebral autoregulation.BJA Open. 2022 Sep 28;4:100093. doi: 10.1016/j.bjao.2022.100093. eCollection 2022 Dec. BJA Open. 2022. PMID: 37588784 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Tale of Two Cities: narrative review of oxygen.F1000Res. 2023 May 9;12:246. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.130592.2. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 37224313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Stepwise Recruitment Maneuvers on Cerebral Hemodynamics: Experimental Study in Neonatal Model.J Pers Med. 2023 Jul 25;13(8):1184. doi: 10.3390/jpm13081184. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37623435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishiyama T, Matsukawa T, Yokoyama T, Hanaoka K. Cerebrovascular carbon dioxide reactivity during general anesthesia: a comparison between sevoflurane and isoflurane. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:1437–1441. - PubMed
-
- Goettel N, Patet C, Rossi A, Burkhart CS, Czosnyka M, Strebel SP, Steiner LA. Monitoring of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in adults undergoing sevoflurane anesthesia: a prospective cohort study of two age groups. J Clin Monit Comput. 2016;30:255–264. doi: 10.1007/s10877-015-9754-z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

