DLL3: an emerging target in small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 31215500
- PMCID: PMC6582566
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-019-0745-2
DLL3: an emerging target in small cell lung cancer
Abstract
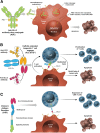
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accounts for approximately 15% of all lung cancers. Despite high rates of response to first-line chemotherapy and radiotherapy, patients with extensive-stage disease eventually relapse, and very few patients survive more than 5 years from diagnosis. Treatment options for recurrent or refractory disease are limited, and the treatments that do exist are associated with significant treatment-related toxicities. Delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3) is an inhibitory Notch ligand that is highly expressed in SCLC and other neuroendocrine tumors but minimally expressed in normal tissues. It is therefore being explored as a potential therapeutic target in SCLC. Here, we review the preclinical and clinical evidence for targeting DLL3 in SCLC and discuss several DLL3-specific therapies being developed for the treatment of SCLC: the antibody-drug conjugate rovalpituzumab tesirine, the bispecific T cell engager immuno-oncology therapy AMG 757, and the chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy AMG 119.
Keywords: Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC); Bispecific T cell engager (BiTE®) antibody construct; Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy; Delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3); Immuno-oncology therapy; Neuroendocrine; Small cell lung cancer (SCLC); Targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.G. and J.M.B. are employed by and hold shares in Amgen Inc. M-A.D.S. is employed by Amgen Inc. D.H.O. and K.H. declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Genentech, Inc. Tecentriq (atezolizumab) [package insert]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/761034s010lbl.pdf. Revised June 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

