Ivermectin reverses the drug resistance in cancer cells through EGFR/ERK/Akt/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 31215501
- PMCID: PMC6580523
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1251-7
Ivermectin reverses the drug resistance in cancer cells through EGFR/ERK/Akt/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Background: Discovery and development of novel drugs that are capable of overcoming drug resistance in tumor cells are urgently needed clinically. In this study, we sought to explore whether ivermectin (IVM), a macrolide antiparasitic agent, could overcome the resistance of cancer cells to the therapeutic drugs.
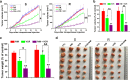
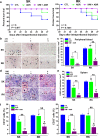
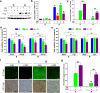
Methods: We used two solid tumor cell lines (HCT-8 colorectal cancer cells and MCF-7 breast cancer cells) and one hematologic tumor cell line (K562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells), which are resistant to the chemotherapeutic drugs vincristine and adriamycin respectively, and two xenograft mice models, including the solid tumor model in nude mice with the resistant HCT-8 cells and the leukemia model in NOD/SCID mice with the resistant K562 cells to investigate the reversal effect of IVM on the resistance in vitro and in vivo. MTT assay was used to investigate the effect of IVM on cancer cells growth in vitro. Flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence were performed to investigate the reversal effect of IVM in vivo. Western blotting, qPCR, luciferase reporter assay and ChIP assay were used to detect the molecular mechanism of the reversal effect. Octet RED96 system and Co-IP were used to determine the interactions between IVM and EGFR.
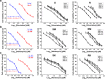
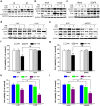
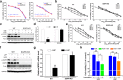
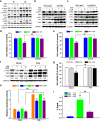
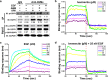
Results: Our results indicated that ivermectin at its very low dose, which did not induce obvious cytotoxicity, drastically reversed the resistance of the tumor cells to the chemotherapeutic drugs both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ivermectin reversed the resistance mainly by reducing the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) via inhibiting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), not by directly inhibiting P-gp activity. Ivermectin bound with the extracellular domain of EGFR, which inhibited the activation of EGFR and its downstream signaling cascade ERK/Akt/NF-κB. The inhibition of the transcriptional factor NF-κB led to the reduced P-gp transcription.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrated that ivermectin significantly enhanced the anti-cancer efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs to tumor cells, especially in the drug-resistant cells. Thus, ivermectin, a FDA-approved antiparasitic drug, could potentially be used in combination with chemotherapeutic agents to treat cancers and in particular, the drug-resistant cancers.
Keywords: Drug resistance; EGFR; Ivermectin; P-glycoprotein; Reversal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ferulic acid reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance via inhibition of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Jan;63:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.09.022. Epub 2018 Oct 12. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30342318
-
Shenmai injection suppresses multidrug resistance in MCF-7/ADR cells through the MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathway.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):276-285. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1742167. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 32251615 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of phosphatase and tensin homology deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) gene transfection on reversal of multidrug resistance in K562/ADM cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2012 Jul;53(7):1383-9. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.650695. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012. PMID: 22185283
-
Therapeutic resistance in breast cancer cells can result from deregulated EGFR signaling.Adv Biol Regul. 2020 Dec;78:100758. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2020.100758. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Adv Biol Regul. 2020. PMID: 33022466 Review.
-
P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-driven cancer drug resistance: biological profile, non-coding RNAs, drugs and nanomodulators.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Nov;29(11):104161. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104161. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 39245345 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr;236(4):2959-2975. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30055. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32959892 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin synergizes sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting multiple oncogenic pathways.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022 Jun;10(3):e00954. doi: 10.1002/prp2.954. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35568994 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin and gemcitabine combination treatment induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells via mitochondrial dysfunction.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 26;13:934746. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.934746. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091811 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin Inhibits Bladder Cancer Cell Growth and Induces Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(5):348-357. doi: 10.2174/0118715206274095231106042833. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38375808
-
Involvement of Multidrug Resistance Modulators in the Regulation of the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Sep 16;12(9):890. doi: 10.3390/membranes12090890. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kartal-Yandim M, Adan-Gokbulut A, Baran Y. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance and its reversal in cancer. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2016;36:716–726. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

