Association Between Childhood Behaviors and Adult Employment Earnings in Canada
- PMID: 31215972
- PMCID: PMC6584893
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.1326
Association Between Childhood Behaviors and Adult Employment Earnings in Canada
Abstract
Importance: Specifying the association between childhood behaviors and adult earnings can inform the development of screening tools and preventive interventions to enhance social integration and economic participation.
Objective: To test the association between behaviors at age 6 years and employment earnings at age 33 to 35 years.
Design, setting, and participants: This study obtained data from the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Kindergarten Children, a population-based sample of boys and girls (n = 3020) born in 1980 or 1981 in Quebec, Canada, and followed up from January 1, 1985, to December 31, 2015. The data included behavioral ratings by kindergarten teachers when the children were aged 5 or 6 years and 2013 to 2015 government tax returns of those same participants at age 33 to 35 years. Data were analyzed from September 2017 to December 2018.
Main outcomes and measures: Mixed-effects linear regression models were used to test the associations between teacher-rated inattention, hyperactivity, aggression, opposition, anxiety, and prosociality at age 6 years and reported annual earnings on income tax returns at age 33 to 35 years. Participant IQ and family adversity were adjusted for in the analysis.
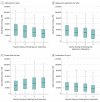
Results: The study included 2850 participants, with a mean (SD) age of 35.9 (0.29) years, of whom 1470 (51.6%) were male and 2740 (96.2%) were white. The mean (SD) personal earnings at follow-up were US $33 300 ($27 500) for men and $19 400 ($15 200) for women. A 1-unit increase in inattention score at age 6 years (males mean [SD], 2.47 [2.42] vs females mean [SD], 1.67 [2.07]) was associated with a decrease in annual earnings of $1271.49 (95% CI, -1908.67 to -634.30) for male participants and $924.25 (95% CI, -1424.44 to -425.46) for female participants. A combined aggression-opposition score (males mean [SD] 2.22 [2.52] vs females mean [SD], 1.05 [1.73]) was associated with a reduction in earnings of $699.83 (95% CI, -1262.49 to -137.17) for males only, albeit with an effect size roughly half that of inattention. A 1-unit increase in prosociality score (males mean [SD], 6.12 [4.30] vs females mean [SD], 7.90 [4.56]) was associated with an increase in earnings of $476.75 (95% CI, 181.53-771.96) for male participants only. A 1-SD reduction in inattention score at age 6 years would theoretically restore $3077 in annual earnings for male participants and $1915 for female participants.
Conclusions and relevance: In this large population-based sample of kindergarten children, behavioral ratings at 5-6 years were associated with employment earnings 3 decades later, independent of a person's IQ and family background. Inattention and aggression-opposition were associated with lower annual employment earnings, and prosociality with higher earnings but only among male participants; inattention was the only behavioral predictor of income among girls. Early monitoring and support for children demonstrating high inattention and for boys exhibiting high aggression-opposition and low prosocial behaviors could have long-term advantages for those individuals and society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Childhood Externalizing, Internalizing, and Comorbid Symptoms With Long-term Economic and Social Outcomes.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jan 3;6(1):e2249568. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.49568. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 36622675 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Behavior in Boys From Low Socioeconomic Neighborhoods With Employment Earnings in Adulthood.JAMA Pediatr. 2019 Apr 1;173(4):334-341. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.5375. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30742199 Free PMC article.
-
Inattention in boys from low-income backgrounds predicts welfare receipt: a 30-year prospective study.Psychol Med. 2020 Sep;50(12):2001-2009. doi: 10.1017/S0033291719002058. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Psychol Med. 2020. PMID: 31481136
-
Mechanisms and pathways linking kindergarten behavior problems with mid-life employment earnings for males from low-income neighborhoods.Child Dev. 2024 Jan-Feb;95(1):208-222. doi: 10.1111/cdev.13967. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Child Dev. 2024. PMID: 37424295
-
Association of Severe Trauma With Work and Earnings in a National Cohort in Canada.JAMA Surg. 2021 Jan 1;156(1):51-59. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.4599. JAMA Surg. 2021. PMID: 33112383 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Monetary Valuation of Children's Cognitive Outcomes in Economic Evaluations from a Societal Perspective: A Review.Children (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;8(5):352. doi: 10.3390/children8050352. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Commentary: On intimate relationships, adult roles, interplay of family adversity and individual vulnerability, intergenerational transmission, and developmental selection - commentary on Vergunst et al. (2020).J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;62(7):853-856. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13393. Epub 2021 Mar 7. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33682144 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Childhood Externalizing, Internalizing, and Comorbid Symptoms With Long-term Economic and Social Outcomes.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jan 3;6(1):e2249568. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.49568. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 36622675 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent depression and subsequent earnings across early to middle adulthood: a 25-year longitudinal cohort study.Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2020 Apr 29;29:e123. doi: 10.1017/S2045796020000360. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2020. PMID: 32345393 Free PMC article.
-
Socioeconomic disparities in suicide: Causation or confounding?PLoS One. 2021 Jan 4;16(1):e0243895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243895. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33395418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knapp M, King D, Healey A, Thomas C. Economic outcomes in adulthood and their associations with antisocial conduct, attention deficit and anxiety problems in childhood. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2011;14(3):137-147. - PubMed
-
- Healey A, Knapp M, Farrington DP. Adult labour market implications of antisocial behaviour in childhood and adolescence: findings from a UK longitudinal study. Appl Econ. 2004;36(2):93-105. doi:10.1080/0003684042000174001 - DOI

