Landscape Characteristics Affecting Spatial Patterns of Water Quality Variation in a Highly Disturbed Region
- PMID: 31216617
- PMCID: PMC6617499
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16122149
Landscape Characteristics Affecting Spatial Patterns of Water Quality Variation in a Highly Disturbed Region
Abstract
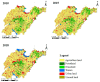
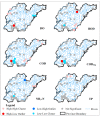
Spatial patterns of water quality trends for 45 stations in control units of the Shandong Province, China during 2009-2017 were examined by a non-parametric seasonal Mann-Kendall's test (SMK) for dissolved oxygen (DO), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), permanganate index (CODMn), total phosphorus (TP) and ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N). The DO concentration showed significant upward trends at approximately half of the stations, while other parameters showed significant downward trends at more than 40% of stations. The stations with downward trends presented significant spatial autocorrelation, and were mainly concentrated in the northwest and southwest regions. The relationship between the landscape characteristics and water quality was explored using stepwise multiple regression models, which indicated the water quality was better explained using landscape pattern metrics compared to the percentage of land use types. Decreased mean patch area and connectedness of farmland will promote the control of BOD, COD and CODMn, whereas the increased landscape percentage of urban areas were not conducive to the water quality improvement, which suggested the sprawling of farmland and urban land was not beneficial to pollution control. Increasing the grassland area was conducive to the reduction of pollutants, while the effect of grassland fragmentation was reversed.
Keywords: landscape patterns; spatial analysis; water quality management; water quality trends.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Aubert A.H., Gascuel-Odoux C., Merot P. Annual hysteresis of water quality: A method to analyse the effect of intra- and inter-annual climatic conditions. J. Hydrol. 2013;478:29–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.027. - DOI
-
- Ahearn D.S., Sheibley R.W., Dahlgren R.A., Keller K.E. Temporal dynamics of stream water chemistry in the last free-flowing river draining the western Sierra Nevada, California. J. Hydrol. 2004;295:47–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.02.016. - DOI
-
- Arheimer B., Lidén R. Nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations from agricultural catchments—Influence of spatial and temporal variables. J. Hydrol. 2000;227:140–159. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00177-8. - DOI
-
- Hongmei B., Xiang T., Siyue L., Quanfa Z. Temporal and spatial variations of water quality in the Jinshui River of the South Qinling Mts. China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010;73:907–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

