Potential of Transcript Editing Across Mitogenomes of Early Land Plants Shows Novel and Familiar Trends
- PMID: 31216623
- PMCID: PMC6627324
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122963
Potential of Transcript Editing Across Mitogenomes of Early Land Plants Shows Novel and Familiar Trends
Abstract
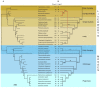
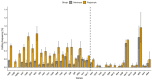
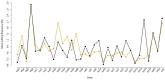
RNA editing alters the identity of nucleotides in an RNA sequence so that the mature transcript differs from the template defined in the genome. This process has been observed in chloroplasts and mitochondria of both seed and early land plants. However, the frequency of RNA editing in plant mitochondria ranges from zero to thousands of editing sites. To date, analyses of RNA editing in mitochondria of early land plants have been conducted on a small number of genes or mitochondrial genomes of a single species. This study provides an overview of the mitogenomic RNA editing potential of the main lineages of these two groups of early land plants by predicting the RNA editing sites of 33 mitochondrial genes of 37 species of liverworts and mosses. For the purpose of the research, we newly assembled seven mitochondrial genomes of liverworts. The total number of liverwort genera with known complete mitogenome sequences has doubled and, as a result, the available complete mitogenome sequences now span almost all orders of liverworts. The RNA editing site predictions revealed that C-to-U RNA editing in liverworts and mosses is group-specific. This is especially evident in the case of liverwort lineages. The average level of C-to-U RNA editing appears to be over three times higher in liverworts than in mosses, while the C-to-U editing frequency of the majority of genes seems to be consistent for each gene across bryophytes.
Keywords: RNA editing; early land plants; liverwort; mitochondrial genome; moss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial genomes of the early land plant lineage liverworts (Marchantiophyta): conserved genome structure, and ongoing low frequency recombination.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 9;20(1):953. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6365-y. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31818248 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear DYW-type PPR gene families diversify with increasing RNA editing frequencies in liverwort and moss mitochondria.J Mol Evol. 2012 Feb;74(1-2):37-51. doi: 10.1007/s00239-012-9486-3. J Mol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22302222
-
The complete plastid genome sequence of the enigmatic moss, Takakia lepidozioides (Takakiopsida, Bryophyta): evolutionary perspectives on the largest collection of genes in mosses and the intensive RNA editing.Plant Mol Biol. 2021 Nov;107(4-5):431-449. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01214-z. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Plant Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34817767
-
Variation in protein gene and intron content among land plant mitogenomes.Mitochondrion. 2020 Jul;53:203-213. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2020.06.002. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Mitochondrion. 2020. PMID: 32535166 Review.
-
Diversity, phylogeny, and adaptation of bryophytes: insights from genomic and transcriptomic data.J Exp Bot. 2022 Jul 16;73(13):4306-4322. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac127. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35437589 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of the Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Apium graveolens and Apium leptophyllum Provide Insights into Evolution and Phylogeny Relationships.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 27;24(19):14615. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914615. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834070 Free PMC article.
-
Complete mitochondrial genome of Agropyron cristatum reveals gene transfer and RNA editing events.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Sep 4;24(1):830. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05558-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39232676 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking the limits - multichromosomal structure of an early eudicot Pulsatilla patens mitogenome reveals extensive RNA-editing, longest repeats and chloroplast derived regions among sequenced land plant mitogenomes.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Mar 9;22(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03492-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35264098 Free PMC article.
-
The Increase of Simple Sequence Repeats during Diversification of Marchantiidae, An Early Land Plant Lineage, Leads to the First Known Expansion of Inverted Repeats in the Evolutionarily-Stable Structure of Liverwort Plastomes.Genes (Basel). 2020 Mar 12;11(3):299. doi: 10.3390/genes11030299. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32178248 Free PMC article.
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of Riccia fluitans L. (Ricciaceae, Marchantiophyta): investigation of intraspecific variations on mitochondrial genomes of R. fluitans.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020 Feb 28;5(2):1220-1222. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1730728. eCollection 2020. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020. PMID: 33366919 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

