The Prediction of Gestational Hypertension, Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction via the First Trimester Screening of Plasma Exosomal C19MC microRNAs
- PMID: 31216670
- PMCID: PMC6627682
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122972
The Prediction of Gestational Hypertension, Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction via the First Trimester Screening of Plasma Exosomal C19MC microRNAs
Abstract
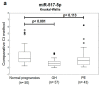
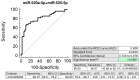
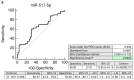
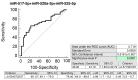
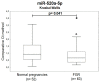
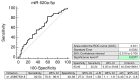
The aim of the study was to verify if quantification of placental specific C19MC microRNAs in plasma exosomes would be able to differentiate during the early stages of gestation between patients subsequently developing pregnancy-related complications and women with the normal course of gestation and if this differentiation would lead to the improvement of the diagnostical potential. The retrospective study on singleton Caucasian pregnancies was performed within 6/2011-2/2019. The case control study, nested in a cohort, involved women that later developed GH (n = 57), PE (n = 43), FGR (n = 63), and 102 controls. Maternal plasma exosome profiling was performed with the selection of C19MC microRNAs with diagnostical potential only (miR-516b-5p, miR-517-5p, miR-518b, miR-520a-5p, miR-520h, and miR-525-5p) using real-time RT-PCR. The down-regulation of miR-517-5p, miR-520a-5p, and miR-525-5p was observed in patients with later occurrence of GH and PE. Maternal plasma exosomal profiling of selected C19MC microRNAs also revealed a novel down-regulated biomarker during the first trimester of gestation (miR-520a-5p) for women destinated to develop FGR. First trimester circulating plasma exosomes possess the identical C19MC microRNA expression profile as placental tissues derived from patients with GH, PE and FGR after labor. The predictive accuracy of first trimester C19MC microRNA screening (miR-517-5p, miR-520a-5p, and miR-525-5p) for the diagnosis of GH and PE was significantly higher in the case of expression profiling of maternal plasma exosomes compared to expression profiling of the whole maternal plasma samples.
Keywords: C19MC microRNA; exosomes; expression; fetal growth restriction; gestational hypertension; plasma; prediction; preeclampsia; pregnancy-related complications; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

