Comparing the Metabolic Capabilities of Bacteria in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex
- PMID: 31216777
- PMCID: PMC6617402
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms7060177
Comparing the Metabolic Capabilities of Bacteria in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex
Abstract
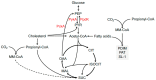
Pathogenic mycobacteria are known for their ability to maintain persistent infections in various mammals. The canonical pathogen in this genus is Mycobacterium tuberculosis and this bacterium is particularly successful at surviving and replicating within macrophages. Here, we will highlight the metabolic processes that M. tuberculosis employs during infection in macrophages and compare these findings with what is understood for other pathogens in the M. tuberculosis complex.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex; carbon metabolism; cholesterol; fatty acids; macrophages; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Niemann S., Richter E., Dalügge-Tamm H., Schlesinger H., Graupner D., Königstein B., Gurath G., Greinert U., Rüsch-Gerdes S. Two cases of Mycobacterium microti derived tuberculosis in HIV-negative immunocompetent patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000;6:539–542. doi: 10.3201/eid0605.000516. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Malone K.M., Gordon S.V. In: Strain Variation in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex.: Its Role in Biology, Epidemiology and Control. Gagneux S., editor. Springer International Publishing AG; Basel, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- Blazquez J., Espinosa de Los Monteros L.E., Samper S., Martín C., Guerrero A., Cobo J., Van Embden J., Baquero F., Gómez-Mampaso E. Genetic characterization of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium bovis strains from a hospital outbreak involving human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997;35:1390–1393. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

