Vasopressin Cells in the Rodent Olfactory Bulb Resemble Non-Bursting Superficial Tufted Cells and Are Primarily Inhibited upon Olfactory Nerve Stimulation
- PMID: 31217196
- PMCID: PMC6620393
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0431-18.2019
Vasopressin Cells in the Rodent Olfactory Bulb Resemble Non-Bursting Superficial Tufted Cells and Are Primarily Inhibited upon Olfactory Nerve Stimulation
Abstract
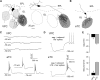
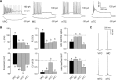
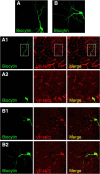
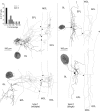
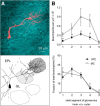
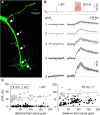
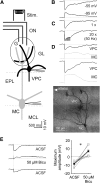
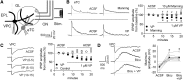
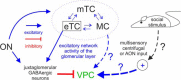
The intrinsic vasopressin system of the olfactory bulb is involved in social odor processing and consists of glutamatergic vasopressin cells (VPCs) located at the medial border of the glomerular layer. To characterize VPCs in detail, we combined various electrophysiological, neuroanatomical, and two-photon Ca2+ imaging techniques in acute bulb slices from juvenile transgenic rats with eGFP-labeled VPCs. VPCs showed regular non-bursting firing patterns, and displayed slower membrane time constants and higher input resistances versus other glutamatergic tufted cell types. VPC axons spread deeply into the external plexiform and superficial granule cell layer (GCL). Axonal projections fell into two subclasses, with either denser local columnar collaterals or longer-ranging single projections running laterally within the internal plexiform layer and deeper within the granule cell layer. VPCs always featured lateral dendrites and a tortuous apical dendrite that innervated a single glomerulus with a homogenously branching tuft. These tufts lacked Ca2+ transients in response to single somatically-evoked action potentials and showed a moderate Ca2+ increase upon prolonged action potential trains.Notably, electrical olfactory nerve stimulation did not result in synaptic excitation of VPCs, but triggered substantial GABAA receptor-mediated IPSPs that masked excitatory barrages with yet longer latency. Exogenous vasopressin application reduced those IPSPs, as well as olfactory nerve-evoked EPSPs recorded from external tufted cells. In summary, VPCs can be classified as non-bursting, vertical superficial tufted cells. Moreover, our findings imply that sensory input alone cannot trigger excitation of VPCs, arguing for specific additional pathways for excitation or disinhibition in social contexts.
Keywords: calcium imaging; electrophysiology; olfactory bulb; social; tufted cells; vasopressin.
Copyright © 2019 Lukas et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subpopulations of Projection Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb.Front Neural Circuits. 2020 Aug 28;14:561822. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2020.561822. eCollection 2020. Front Neural Circuits. 2020. PMID: 32982699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organization of inhibition in the rat olfactory bulb external plexiform layer.J Neurophysiol. 1993 Jul;70(1):263-74. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.1.263. J Neurophysiol. 1993. PMID: 8395579
-
Vasopressin differentially modulates the excitability of rat olfactory bulb neuron subtypes.Front Neural Circuits. 2024 Aug 29;18:1448592. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2024.1448592. eCollection 2024. Front Neural Circuits. 2024. PMID: 39268350 Free PMC article.
-
Current-source density analysis in the rat olfactory bulb: laminar distribution of kainate/AMPA- and NMDA-receptor-mediated currents.J Neurophysiol. 1999 Jan;81(1):15-28. doi: 10.1152/jn.1999.81.1.15. J Neurophysiol. 1999. PMID: 9914263
-
Functional organization of the main olfactory bulb.Microsc Res Tech. 1993 Feb 1;24(2):142-56. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070240206. Microsc Res Tech. 1993. PMID: 8457726 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of projection neuron subtypes in the mouse olfactory bulb.Elife. 2021 Jul 22;10:e65445. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65445. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34292150 Free PMC article.
-
Top-down acetylcholine signaling via olfactory bulb vasopressin cells contributes to social discrimination in rats.Commun Biol. 2021 May 21;4(1):603. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02129-7. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34021245 Free PMC article.
-
Subpopulations of Projection Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb.Front Neural Circuits. 2020 Aug 28;14:561822. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2020.561822. eCollection 2020. Front Neural Circuits. 2020. PMID: 32982699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasopressin receptor 1a, oxytocin receptor, and oxytocin knockout male and female mice display normal perceptual abilities towards non-social odorants.Horm Behav. 2023 Feb;148:105302. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2022.105302. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Horm Behav. 2023. PMID: 36628861 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical and Functional Connectivity at the Dendrodendritic Reciprocal Mitral Cell-Granule Cell Synapse: Impact on Recurrent and Lateral Inhibition.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 Jul 22;16:933201. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.933201. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 35937203 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
