A "Set Point" for Water Homeostasis Disturbed with Altered Kidney Transplantation Outcome
- PMID: 31217326
- PMCID: PMC6622427
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019050472
A "Set Point" for Water Homeostasis Disturbed with Altered Kidney Transplantation Outcome
Keywords: median pre-optic nucleus; thirst; water homeostasis; water load.
Figures
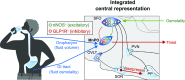
Comment on
-
Osmoregulation Performance and Kidney Transplant Outcome.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Jul;30(7):1282-1293. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018121269. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31217325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bichet D, Szatalowicz V, Chaimovitz C, Schrier RW: Role of vasopressin in abnormal water excretion in cirrhotic patients. Ann Intern Med 96: 413–417, 1982 - PubMed
-
- Kern PA, Robbins RJ, Bichet D, Berl T, Verbalis JG: Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis in the absence of arginine vasopressin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 62: 148–152, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Bichet DG, Kortas C, Mettauer B, Manzini C, Marc-Aurèle J, Rouleau JL, et al. .: Modulation of plasma and platelet vasopressin by cardiac function in patients with heart failure. Kidney Int 29: 1188–1196, 1986 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

