SMPDL3b modulates insulin receptor signaling in diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 31217420
- PMCID: PMC6584700
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10584-4
SMPDL3b modulates insulin receptor signaling in diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase acid-like 3b (SMPDL3b) is a lipid raft enzyme that regulates plasma membrane (PM) fluidity. Here we report that SMPDL3b excess, as observed in podocytes in diabetic kidney disease (DKD), impairs insulin receptor isoform B-dependent pro-survival insulin signaling by interfering with insulin receptor isoforms binding to caveolin-1 in the PM. SMPDL3b excess affects the production of active sphingolipids resulting in decreased ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P) content as observed in human podocytes in vitro and in kidney cortexes of diabetic db/db mice in vivo. Podocyte-specific Smpdl3b deficiency in db/db mice is sufficient to restore kidney cortex C1P content and to protect from DKD. Exogenous administration of C1P restores IR signaling in vitro and prevents established DKD progression in vivo. Taken together, we identify SMPDL3b as a modulator of insulin signaling and demonstrate that supplementation with exogenous C1P may represent a lipid therapeutic strategy to treat diabetic complications such as DKD.
Conflict of interest statement
G.W.B., A.F., and S.M. are inventors on pending or issued patents (US10,183,038, US10,052,345) aimed to diagnose or treat proteinuric renal diseases. They stand to gain royalties from their future commercialization. A.F. is Chief Scientific Officer of L&F Health LLC and is consultant for Variant Pharmaceutical. Variant Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has licensed worldwide rights to develop and commercialize hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin for treatment of kidney disease from L&F Research. S.M. holds equity interest in a company presently commercializing the form of cyclodextrin referenced in this paper. The patent associated with the use of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin is published under US10,195,227. A.F. is Chief Medical Officer of LipoNexT, LLC. The remaining authors delare no competing interests.
Figures
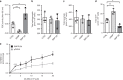
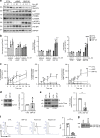
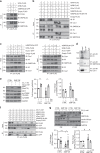
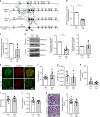
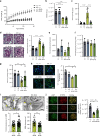
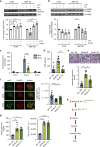
Comment in
-
Podocyte lipotoxicity in diabetic kidney disease.Kidney Int. 2019 Oct;96(4):809-812. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.07.013. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 31543147 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 DK076169/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK083912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK100846/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000460/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK104753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA227493/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128714/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK117599/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK081943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK115109/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090316/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

