Clinical features, follow-up, and reprogramming of patients with pacemaker in a secondary care center
- PMID: 31217679
- PMCID: PMC6548520
Clinical features, follow-up, and reprogramming of patients with pacemaker in a secondary care center
Abstract
Introduction: During recent years, several recommendations and guidelines regarding cardiac pacing have been published in the literature. However, only a few studies have examined the implementation of these guidelines in clinical practice. The current study aimed to record and evaluate the effects of the mainstream studies, and the experience gathered by all patients who have been followed-up at the pacemaker Unit of Veroia Hospital, which is a secondary care center.
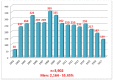
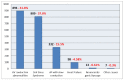
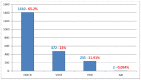
Methods and results: Epidemiological, clinical, and electrocardiographic data were collected and studied for patients with a permanent pacemaker that have been followed-up in our hospital from 2002 to 2017. The total number of patients of the study was 3,902 (2,164 men; 55.45 %) with a mean age of 73.4 ± 12.6 years. Third degree atrioventricular (AV) block was the most common cause of pacing. Dysfunction of the sinus node involved the majority of cases with bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome. At 18 patients, the cause of permanent pacemaker implantation was carotid sinus syndrome and at 13 of them, cardio-vascular type of neurocardiogenic syncope. Dizziness and syncope were the most common symptoms. Dual-chamber pacing was the most common type of pacing, which has been increasing in recent years. In follow-up visits, the most frequent examinations concerned battery condition, as the stimulation and sensing threshold. Reprogramming of the device was required in 1,434 patients (36.75 %), especially during the first year after implantation.
Conclusion: Pacing indications have been unchanged during all the years of the study and have been based on confirmed bradycardia and major symptoms. Reprogramming of the device was needed in an increased number of patients. HIPPOKRATIA 2018, 22(2): 75-79.
Keywords: Pacemaker; follow-up; reprogramming; secondary care center.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of internal audit on pacemaker prescription and the immediate costs of pacing in the northern region: towards implementation of the recommendations of the British Pacing and Electrophysiology Group.Br Heart J. 1994 Apr;71(4):395-8. doi: 10.1136/hrt.71.4.395. Br Heart J. 1994. PMID: 8198896 Free PMC article.
-
Trend of the main clinical characteristics and pacing modality in patients treated by pacemaker: data from the Italian Pacemaker Registry for the quinquennium 2003-07.Europace. 2010 Feb;12(2):202-9. doi: 10.1093/europace/eup346. Epub 2009 Nov 9. Europace. 2010. PMID: 19903671
-
Dual chamber cardiac pacing in children: Single chamber pacing dual chamber sensing cardiac pacemaker or dual chamber pacing and sensing cardiac pacemaker?Pediatr Int. 2002 Dec;44(6):635-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-200x.2002.01631.x. Pediatr Int. 2002. PMID: 12421261
-
[Treatment of bradycardias - who needs a pacemaker?].Ther Umsch. 2014 Feb;71(2):105-10. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930/a000489. Ther Umsch. 2014. PMID: 24463380 Review. German.
-
Clinically oriented device programming in bradycardia patients: part 2 (atrioventricular blocks and neurally mediated syncope). Proposals from AIAC (Italian Association of Arrhythmology and Cardiac Pacing).J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2018 Apr;19(4):170-180. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000629. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2018. PMID: 29470251 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond the Pain Management Clinic: The Role of AI-Integrated Remote Patient Monitoring in Chronic Disease Management - A Narrative Review.J Pain Res. 2024 Dec 11;17:4223-4237. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S494238. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39679431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Udo EO, van Hemel NM, Zuithoff NP, Barrett MJ, Ruiter JH, Doevendans PA, et al. Incidence and predictors of pacemaker reprogramming: potential consequences for remote follow-up. Europace. 2013;15:978–983. - PubMed
-
- Curila K, Smida J, Herman D, Osmancik P, Stros P, Zdarska J, et al. Pacemaker reprogramming rarely needed after device replacement. Herz. 2019;44:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Peal JE, Mathews IG, Runnett C, Thomas HE, Ripley DP. An update on cardiac implantable electronic devices for the general physician. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2018;48:141–147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
