Comparing progression molecular mechanisms between lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma based on genetic and epigenetic networks: big data mining and genome-wide systems identification
- PMID: 31217907
- PMCID: PMC6557199
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26940
Comparing progression molecular mechanisms between lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma based on genetic and epigenetic networks: big data mining and genome-wide systems identification
Abstract
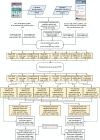
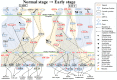
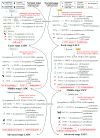
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the predominant type of lung cancer in the world. Lung adenocarcinoma (LADC) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) are subtypes of NSCLC. We usually regard them as different disease due to their unique molecular characteristics, distinct cells of origin and dissimilar clinical response. However, the differences of genetic and epigenetic progression mechanism between LADC and LSCC are complicated to analyze. Therefore, we applied systems biology approaches and big databases mining to construct genetic and epigenetic networks (GENs) with next-generation sequencing data of LADC and LSCC. In order to obtain the real GENs, system identification and system order detection are conducted on gene regulatory networks (GRNs) and protein-protein interaction networks (PPINs) for each stage of LADC and LSCC. The core GENs were extracted via principal network projection (PNP). Based on the ranking of projection values, we got the core pathways in respect of KEGG pathway. Compared with the core pathways, we found significant differences between microenvironments, dysregulations of miRNAs, epigenetic modifications on certain signaling transduction proteins and target genes in each stage of LADC and LSCC. Finally, we proposed six genetic and epigenetic multiple-molecule drugs to target essential biomarkers in each progression stage of LADC and LSCC, respectively.
Keywords: NSCLC; genetic and epigenetic network; lung adenocarcinoma; lung squamous cell carcinoma; potential drug target.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Borghaei H, Chang AC, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D’Amico TA, Demmy TL, Govindan R, Grannis FW Jr, Grant SC, Horn L, Jahan TM, et al. , and National comprehensive cancer network . Non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2013. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2013; 11:645–53. 10.6004/jnccn.2013.0084. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

