Challenges and solutions in patient treatment strategies for stage II colon cancer
- PMID: 31217978
- PMCID: PMC6573795
- DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goz006
Challenges and solutions in patient treatment strategies for stage II colon cancer
Abstract
Colorectal cancer remains one of the most common cancers worldwide and, despite improvements in treatment options for late-stage metastatic cancer, there are still questions surrounding how best to treat early-stage disease patients. Some recent advances have been made in the staging of cancer and improving the risk assessment of strategies for patient treatment. A number of high-risk features have been proposed that may help to stratify stage II cancer patients into groups that will truly benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy. Diagnostic tests are becoming available to measure these biomarkers, utilizing both currently available and novel technologies. This review will describe the challenges in treatment decisions for early-stage colon cancer and how personalized medicine can assist clinicians in making the best treatment choices for patients with stage II colon cancer in particular.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; challenge; treatment strategy.
Figures
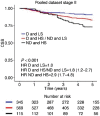
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I. et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- https://www.wcrf.org/int/cancer-facts-figures/data-specific-cancers/colo... (October 2018, date last accessed).
-
- http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/st... (October 2018, date last accessed).
-
- Luengo-Fernandez R, Leal J, Gray A. et al. Economic burden of cancer across the European Union: a population-based cost analysis. Lancet Oncol 2013;14:1165–74. - PubMed
-
- Gray R, Barnwell J. et al. Quasar Collaborative Group Adjuvant chemotherapy versus observation in patients with colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Lancet 2007;370:2020–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

