Impella versus IABP in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock
- PMID: 31218000
- PMCID: PMC6546200
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2018-000987
Impella versus IABP in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock
Erratum in
-
Correction: Impella versus IABP in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock.Open Heart. 2019 Jun 24;6(1):e000987corr1. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2018-000987corr1. eCollection 2019. Open Heart. 2019. PMID: 31297229 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the benefit of Impella, a modern percutaneous mechanical support (pMCS) device, versus former standard intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock (AMICS).
Methods: This single-centre, retrospective study included patients with AMICS receiving pMCS with either Impella or IABP. Disease severity at baseline was assessed with the IABP-SHOCK II score. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality at 30 days. Secondary outcomes were parameters of shock severity at the early postimplantation phase. Adjusted Cox proportional hazards models identified independent predictors of the primary outcome.
Results: Of 116 included patients, 62 (53%) received Impella and 54 (47%) IABP. Despite similar baseline mortality risk (IABP-SHOCK II high-risk score of 18 % vs 20 %; p = 0.76), Impella significantly reduced the inotropic score (p < 0.001), lactate levels (p < 0.001) and SAPS II (p =0.02) and improved left ventricular ejection fraction (p = 0.01). All-cause mortality at 30 days was similar with Impella and IABP (52 % and 67 %, respectively; p = 0.13), but bleeding complications were more frequent in the Impella group (3 vs 4 units of transfused erythrocytes concentrates due to bleeding complications, p = 0.03). Previous cardiopulmonary resuscitation (HR 3.22, 95% CI 1.76 to 5.89; p < 0.01) and an estimated intermediate (HR 2.77, 95% CI 1.42 to 5.40; p < 0.01) and high (HR 4.32 95% CI 2.03 to 9.24; p = 0.01) IABP-SHOCK II score were independent predictors of all-cause mortality.
Conclusions: In patients with AMICS, haemodynamic support with the Impella device had no significant effect on 30-day mortality as compared with IABP. In these patients, large randomised trials are warranted to ascertain the effect of Impella on the outcome.
Keywords: IABP; cardiogenic shock; impella; mechanical support; myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT: Dr Carsten Skurk has perceived lecturer fees from Abiomed, outside the submitted work. Dr Landmesser reports grants from Edwards Lifesciences, grants and personal fees from Abbott, outside the submitted work. All other authors report no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures

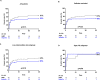

References
-
- Kolh P, Windecker S, Alfonso F, et al. . 2014 ESC/EACTS guidelines on myocardial revascularization: the task Force on myocardial revascularization of the European Society of cardiology (ESC) and the European association for Cardio-Thoracic surgery (EACTS). developed with the special contribution of the European association of percutaneous cardiovascular interventions (EAPCI). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2014;46:517–92. 10.1093/ejcts/ezu366 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
