Communicating uncertainty about facts, numbers and science
- PMID: 31218028
- PMCID: PMC6549952
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.181870
Communicating uncertainty about facts, numbers and science
Abstract
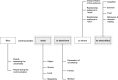
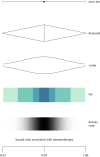
Uncertainty is an inherent part of knowledge, and yet in an era of contested expertise, many shy away from openly communicating their uncertainty about what they know, fearful of their audience's reaction. But what effect does communication of such epistemic uncertainty have? Empirical research is widely scattered across many disciplines. This interdisciplinary review structures and summarizes current practice and research across domains, combining a statistical and psychological perspective. This informs a framework for uncertainty communication in which we identify three objects of uncertainty-facts, numbers and science-and two levels of uncertainty: direct and indirect. An examination of current practices provides a scale of nine expressions of direct uncertainty. We discuss attempts to codify indirect uncertainty in terms of quality of the underlying evidence. We review the limited literature about the effects of communicating epistemic uncertainty on cognition, affect, trust and decision-making. While there is some evidence that communicating epistemic uncertainty does not necessarily affect audiences negatively, impact can vary between individuals and communication formats. Case studies in economic statistics and climate change illustrate our framework in action. We conclude with advice to guide both communicators and future researchers in this important but so far rather neglected field.
Keywords: IPCC; economic statistics; epistemic uncertainty; grade; uncertainty communication.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- 2018. Cambridge dictionary. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Manski CF. 2007. Identification for prediction and decision. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
-
- The British Government. 2003. Iraq's weapons of mass destruction: the Assessment of the British Government.
-
- Butler P, Chilcot J, Inge L, Mates M, Taylor A. 2004. Review of intelligence on weapons of mass destruction. House Commons Comm. Rep.
-
- Walpole RD, Pillar P, Gershwin LK, Landry JR. . 2002. Iraq's Continuing Programs for Weapons of Mass Destruction.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

