Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase dependent cell migration and invasion are dispensable for tumor metastasis
- PMID: 31218104
- PMCID: PMC6556613
Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase dependent cell migration and invasion are dispensable for tumor metastasis
Abstract
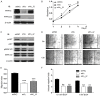
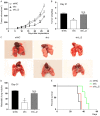
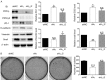
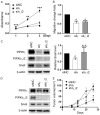
Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase (PIPKIγ) has been associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients by promoting metastasis. Among the six alternative-splicing isoforms of PIPKIγ, PIPKIγ_i2 specifically targets to focal adhesions and regulates focal adhesion turnover, thus was proposed responsible for tumor metastasis. In the present study, we specifically depleted PIPKIγ_i2 from mouse triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) 4T1 cells and analyzed their behaviors. As expected, PIPKIγ_i2-depleted 4T1 cells exhibited reduced proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro at a comparable level as pan-PIPKIγ depleted cells. However, PIPKIγ_i2 depletion had no effect on metastasis and progression of 4T1 tumors in vivo. PIPKIγ_i2-depleted tumors showed similar levels of growth, hypoxia state, macrophage infiltration, and angiogenesis as parental tumors, although the pan-PIPKIγ depletion led to substantial inhibition on these aspects. Further investigation revealed that depleting PIPKIγ_i2 alone, unlike depleting all PIPKIγ isoforms, had no effect on PD-L1 expression, the status of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and the anchorage-independent growth of 4T1 cells. In human TNBC MDA-MB-231 cells, we obtained similar results. Thus, while PIPKIγ_i2 indeed is required for cell migration and invasion, these characteristics are not decisive for metastasis. Other PIPKIγ isoform(s) that regulate the expression of key factors to support cell survival under stresses is more critical for the malignant progression of TNBCs.
Keywords: PIPKIγ; cell migration; metastasis; the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; triple negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase inhibits breast cancer metastasis.Oncogene. 2015 Aug 27;34(35):4635-46. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.393. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25486426 Free PMC article.
-
Type I gamma phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase modulates invasion and proliferation and its expression correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(1):R6. doi: 10.1186/bcr2471. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Breast Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20074374 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative phenotypic analysis of the two major splice isoforms of phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase type Iγ in vivo.J Cell Sci. 2012 Dec 1;125(Pt 23):5636-46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102145. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22976293
-
Silencing of type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase suppresses ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jul;38(1):253-262. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5670. Epub 2017 May 25. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28560454 Free PMC article.
-
Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase promotes tumor growth by facilitating Warburg effect in colorectal cancer.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jun;44:375-386. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.015. Epub 2019 May 16. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31105034 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The functional roles of the circRNA/Wnt axis in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2022 May 5;21(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01582-0. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35513849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of NRF2 by stably associated phosphoinositides and small heat shock proteins in response to stress.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jul;301(7):110367. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110367. Epub 2025 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40516875 Free PMC article.
-
BIBR1532 inhibits proliferation and enhances apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells by reducing telomerase activity.PeerJ. 2023 Nov 8;11:e16404. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16404. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37953768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Doughman RL, Firestone AJ, Anderson RA. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases put PI4,5P(2) in its place. J Membr Biol. 2003;194:77–89. - PubMed
-
- van den Bout I, Divecha N. PIP5K-driven PtdIns(4,5)P2 synthesis: regulation and cellular functions. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3837–3850. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
