eIF3a mediates HIF1α-dependent glycolytic metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through translational regulation
- PMID: 31218114
- PMCID: PMC6556603
eIF3a mediates HIF1α-dependent glycolytic metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through translational regulation
Abstract
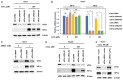
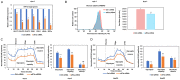
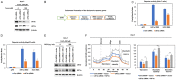
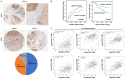
eIF3a is the largest subunit of eIF3 complex and is a key player in translational control. Recently eIF3a is recognized as a proto-oncogene, which is overexpressed and connected to tumorigenesis of many cancers. However, the mechanistic roles of eIF3a during the tumorigenesis remain largely elusive. Here, we report that depletion of eIF3a significantly reduced HIF1α protein level and cellular glycolysis ability. Mechanistically, we found that eIF3a regulates HIF1α protein synthesis through internal ribosomal entry site (IRES)-dependent translation. Importantly, through analyses of our own sample collection, we found that eIF3a is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, and a high level of eIF3a predicts poor prognosis of HCC patients. TCGA analyses further confirmed that eIF3a is coincident with an elevated activity of HIF1α pathway genes. Collectively, we identify eIF3a as a regulator for glycolysis through HIF1α IRES-dependent translational regulation, which may be a potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: HCC; HIF1α; eIF3a; glycolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The translational regulator eIF3a: the tricky eIF3 subunit!Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Dec;1806(2):275-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20647036 Review.
-
eIF3a: A new anticancer drug target in the eIF family.Cancer Lett. 2018 Jan 1;412:81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.055. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29031564 Review.
-
Translation initiation factor eIF3a regulates glucose metabolism and cell proliferation via promoting small GTPase Rheb synthesis and AMPK activation.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jul;298(7):102044. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102044. Epub 2022 May 18. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35595099 Free PMC article.
-
USP29-mediated HIF1α stabilization is associated with Sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by upregulating glycolysis.Oncogenesis. 2021 Jul 16;10(7):52. doi: 10.1038/s41389-021-00338-7. Oncogenesis. 2021. PMID: 34272356 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA screening from EIF3a in lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2019 Aug;8(9):4159-4168. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2338. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31197975 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: Challenges and therapeutic opportunities.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Sep;42(3):741-764. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10071-1. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 36547748 Review.
-
Translation reprogramming by eIF3 linked to glioblastoma resistance.NAR Cancer. 2020 Sep 17;2(3):zcaa020. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcaa020. eCollection 2020 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2020. PMID: 34316689 Free PMC article.
-
3'quant mRNA-Seq of Porcine Liver Reveals Alterations in UPR, Acute Phase Response, and Cholesterol and Bile Acid Metabolism in Response to Different Dietary Fats.Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep 18;11(9):1087. doi: 10.3390/genes11091087. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32961898 Free PMC article.
-
Role of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) Methylation Regulators in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 7;11:755206. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.755206. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34692544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EIF3m promotes the malignant phenotype of lung adenocarcinoma by the up-regulation of oncogene CAPRIN1.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 1;11(3):979-996. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33791168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong Z, Zhang JT. Initiation factor eIF3 and regulation of mRNA translation, cell growth, and cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006;59:169–180. - PubMed
-
- Browning KS, Gallie DR, Hershey JW, Hinnebusch AG, Maitra U, Merrick WC, Norbury C. Unified nomenclature for the subunits of eukaryotic initiation factor 3. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
