Cloning and characterization of special HMW glutenin subunit genes from Aegilops longissima L. and their potential for wheat quality improvement
- PMID: 31218178
- PMCID: PMC6570732
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-019-1803-8
Cloning and characterization of special HMW glutenin subunit genes from Aegilops longissima L. and their potential for wheat quality improvement
Abstract
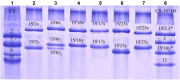
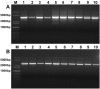
Identification and cloning of new glutenin genes from wheat-related species can provide candidate gene resources for quality improvement of wheat. In this study, ten special high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GS), including five x-type (1Sl2x, 1Sl16x, 1Sl17x, 1Sl23x, and 1Sl25x) and five y-type (1Sl2y, 1Sl6y1, 1Sl16y, 1Sl17y, and 1Sl23y) from Aegilops longissima L. (SlSl, 2n = 2x = 14) were identified, and their complete encoding genes were cloned by allelic-specific polymerase chain reaction (AS-PCR). The deduced amino acid (aa) residues of the x-type subunit genes ranged from 821 aa (2469 bp) to 941 aa (2829 bp), while those of the y-type subunit genes varied from 749 aa (2250 bp) to 771 aa (2361 bp). These special HMW-GS had a longer central repetitive domain with more glutamine repeats and glutamine residues compared to the previously characterized HMW-GS in common wheat, which provided a structural basis for superior gluten quality formation. The authenticity of the four cloned genes were verified by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS). Abundant single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and insertion/deletion (InDel) variations among these genes were identified, which would benefit for developing specific molecular markers used for wheat gluten quality improvement. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the 1Sl-encoded HMW-GS had close relationships with those from bread wheat, which were divergent from Triticum species at 2.10-10.00 million years ago. Our results indicate that the 1Sl genome contains superior candidate glutenin genes that have potential application values for the improvement of wheat bread making quality.
Keywords: AS-PCR; Aegilops longissima L.; Gluten quality; HMW-GS; MALDI-TOF/TOF–MS; Phylogenetics.
Figures



References
-
- Alberto C, Renato D, Antonio TO, Carla C, Marina P, Enrico P. Genetic analysis of the Aegilops longissima, 3S chromosome carrying the Pm13, resistance gene. Euphytica. 2003;130:177–183. doi: 10.1023/A:1022873822114. - DOI
-
- Bekes F, Gras PW, Gupta RB. The effects of purified cereal polypeptides on the mixing properties of dough. In: Williams YA, Wrigley CW, editors. Capturing the benefits of research for consumers. Cereal Chem Div: R. Aust. Chem. Inst; 1995. pp. 92–98.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

