Proteome Profile of Endogenous Retrotransposon-Associated Complexes in Human Embryonic Stem Cells
- PMID: 31219246
- PMCID: PMC8054700
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201900169
Proteome Profile of Endogenous Retrotransposon-Associated Complexes in Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Abstract
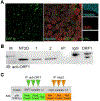
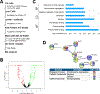
Long Interspersed Element-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are transposable elements similar to retroviruses that have existed in the genome of primates for millions of years. They encode two Open Reading Frame (ORF) proteins (ORF1p and ORF2p) that bind L1 RNA to form a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex and are required for L1 integration into the host genome. Humans have evolved with L1 and found ways to limit L1 activity. To identify partners of the L1 RNP, previous studies used ectopic expression of L1 ORF1/2p or RNA in various cancer cells, which express low levels of the ORF proteins. Whether naturally occurring L1 RNP interacts with the same proteins in non-cancer cells is unknown. Here, the aim is to examine the natural assembly of endogenous L1 RNPs in normal human cells. L1 elements are expressed in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), derived from pre-implantation embryos. Therefore, these cells are used to immunoprecipitate ORF1p followed by MS to identify proteins that associate with the naturally-occurring L1 ORF1p. Some of the same proteins as well as unique proteins are found interacting with the endogenous L1 ORF1p complexes. The analysis of ORF1p-associated proteins in hESCs can help address important questions in both retrotransposon biology and the biology of hESCs.
Keywords: human embryonic stem cells; immunoprecipitation; long interspersed element-1; mass spectrometry; retrotransposition; ribonucleoprotein complex.
© 2019 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of LINE-1 ribonucleoprotein particles.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 7;6(10):e1001150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001150. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20949108 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment of processed pseudogene transcripts in L1-ribonucleoprotein particles.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Sep 15;22(18):3730-48. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt225. Epub 2013 May 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23696454 Free PMC article.
-
Condensation of LINE-1 is critical for retrotransposition.Elife. 2023 Apr 28;12:e82991. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82991. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37114770 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Transcriptional Control of LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Cellular Host Factors in Somatic Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Mar 7;4:14. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00014. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27014690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-nucleic acid interactions of LINE-1 ORF1p.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Feb;86:140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.03.019. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29596909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rewiring of SINE-MIR enhancer topology and Esrrb modulation in expanded and naive pluripotency.Genome Biol. 2025 Apr 28;26(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13059-025-03577-8. Genome Biol. 2025. PMID: 40296153 Free PMC article.
-
A review of strategies used to identify transposition events in plant genomes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 1;13:1080993. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1080993. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36531345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted detection of endogenous LINE-1 proteins and ORF2p interactions.Mob DNA. 2025 Feb 6;16(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13100-024-00339-4. Mob DNA. 2025. PMID: 39915890 Free PMC article.
-
LINE-1 ORF2p expression is nearly imperceptible in human cancers.Mob DNA. 2019 Dec 31;11:1. doi: 10.1186/s13100-019-0191-2. eCollection 2020. Mob DNA. 2019. PMID: 31892958 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity-Based Interactome Analysis of Endogenous LINE-1 Macromolecules.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2607:215-256. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2883-6_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36449166

