Metabolomics in serum of patients with non-advanced age-related macular degeneration reveals aberrations in the glutamine pathway
- PMID: 31220133
- PMCID: PMC6586309
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218457
Metabolomics in serum of patients with non-advanced age-related macular degeneration reveals aberrations in the glutamine pathway
Abstract
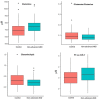
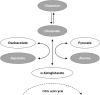
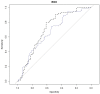
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common, progressive multifactorial vision-threatening disease and many genetic and environmental risk factors have been identified. The risk of AMD is influenced by lifestyle and diet, which may be reflected by an altered metabolic profile. Therefore, measurements of metabolites could identify biomarkers for AMD, and could aid in identifying high-risk individuals. Hypothesis-free technologies such as metabolomics have a great potential to uncover biomarkers or pathways that contribute to disease pathophysiology. To date, only a limited number of metabolomic studies have been performed in AMD. Here, we aim to contribute to the discovery of novel biomarkers and metabolic pathways for AMD using a targeted metabolomics approach of 188 metabolites. This study focuses on non-advanced AMD, since there is a need for biomarkers for the early stages of disease before severe visual loss has occurred. Targeted metabolomics was performed in 72 patients with early or intermediate AMD and 72 control individuals, and metabolites predictive for AMD were identified by a sparse partial least squares discriminant analysis. In our cohort, we identified four metabolite variables that were most predictive for early and intermediate stages of AMD. Increased glutamine and phosphatidylcholine diacyl C28:1 levels were detected in non-advanced AMD cases compared to controls, while the rate of glutaminolysis and the glutamine to glutamate ratio were reduced in non-advanced AMD. The association of glutamine with non-advanced AMD corroborates a recent report demonstrating an elevated glutamine level in early AMD using a different metabolomics technique. In conclusion, this study indicates that metabolomics is a suitable method for the discovery of biomarker candidates for AMD. In the future, larger metabolomics studies could add to the discovery of novel biomarkers in yet unknown AMD pathways and expand our insights in AMD pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The commercial affiliation of S.F. to La Roche AG does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of biofluid metabolomic profiles to the discovery of biomarkers in age-related macular degeneration.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2024 Dec 24;9(1):e001573. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2023-001573. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39719382 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Systematic Review.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Dec 1;61(14):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.14.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 33315052 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Metabolomics of Intermediate and Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Patients.Cells. 2021 Nov 12;10(11):3141. doi: 10.3390/cells10113141. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831363 Free PMC article.
-
Human plasma metabolomics in age-related macular degeneration (AMD) using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.PLoS One. 2017 May 18;12(5):e0177749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177749. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542375 Free PMC article.
-
Human Plasma Metabolomics Study across All Stages of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Identifies Potential Lipid Biomarkers.Ophthalmology. 2018 Feb;125(2):245-254. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.08.008. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Ophthalmology. 2018. PMID: 28916333 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of biofluid metabolomic profiles to the discovery of biomarkers in age-related macular degeneration.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2024 Dec 24;9(1):e001573. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2023-001573. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39719382 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose Metabolic Characterization of Human Aqueous Humor in Relation to Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Mar 9;61(3):49. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.3.49. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32232346 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Systematic Review.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Dec 1;61(14):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.14.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 33315052 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Metabolites Associated with OCT Features of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Ophthalmol Sci. 2023 Jul 1;4(1):100357. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2023.100357. eCollection 2024 Jan-Feb. Ophthalmol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37869026 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Metabolomic Profiles Associated with Three-Year Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Metabolites. 2022 Jan 1;12(1):32. doi: 10.3390/metabo12010032. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35050154 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

