Text messaging support for patients with diabetes or coronary artery disease (SupportMe): protocol for a pragmatic randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 31221870
- PMCID: PMC6589039
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025923
Text messaging support for patients with diabetes or coronary artery disease (SupportMe): protocol for a pragmatic randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Low-cost interventions providing self-management support are needed for people with coronary artery disease (CAD) and diabetes. Mobile phone text messaging provides a potential vehicle for this. The SupportMe Trial aims to assess the feasibility of embedding a text messaging programme into routine clinical practice and will determine if this improves cardiovascular risk factor and diabetes control among patients with CAD or type 2 diabetes.
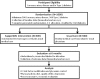
Methods and analysis: SupportMe is a randomised controlled trial to be conducted within the framework of a health district-wide integrated care programme for people with CAD or type 2 diabetes mellitus. One thousand subjects will be recruited, with at least 500 in each group. Intervention subjects will receive four text messages a week for 6 months, which provide advice, motivation, information and support for disease management and healthy behaviour. The primary outcome is systolic blood pressure at 6 months. Secondary outcomes include body mass index, waist circumference, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, physical activity levels, dietary intake, quality of life, mood and smoking cessation, and for subjects with diabetes, glycosylated haemoglobin and fasting serum glucose. A process and economic evaluation will also be conducted.
Ethics and dissemination: The study has been approved by the Western Sydney Local Health District Human Research Ethics Committee (AU RED HREC/16/WMEAD/331). Results will be disseminated via the scientific forums including peer-reviewed publications and presentations at national and international conferences.
Trial registration number: ACTRN12616001689460.
Keywords: clinical trials; coronary heart disease; general diabetes; telemedicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016;388:1459–544. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014. Geneva: WHO, 2016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous