Preparation of a magnetic graphene/polydopamine nanocomposite for magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction of benzoylurea insecticides in environmental water samples
- PMID: 31222032
- PMCID: PMC6586854
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-45186-z
Preparation of a magnetic graphene/polydopamine nanocomposite for magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction of benzoylurea insecticides in environmental water samples
Abstract
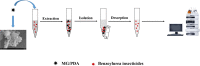
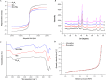
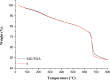
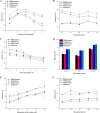
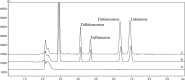
A magnetic graphene/polydopamine (MG/PDA) nanocomposite has been prepared and used as sorbent for magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction (MDSPE) of four benzoylurea insecticides in environmental water samples. The obtained nanocomposites were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, powder X-ray diffraction, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, surface area and porosity analysis and thermogravimetric analysis. To investigate the adsorption performance of MG/PDA for target analytes, various parameters affecting the MG/PDA-based MDSPE procedure were optimized. Under the optimal conditions, the established method exhibits good linearity (R2 ≥ 0.9988) in the concentration range 2.5-500 µg L-1. A low limit of detection (0.75 µg L-1, signal/noise = 3:1), a low limit of quantification (2.50 µg L-1, signal/noise = 10:1), and good precision (intraday relative standard deviation ≤3.6%, interday relative standard deviation ≤4.5%) are also achieved. Finally, the simple, fast, and sensitive sample preparation technique was successfully used to determine benzoylurea insecticides in environmental water samples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Matsumura F. Studies on the action mechanism of benzoylurea insecticides to inhibit the process of chitin synthesis in insects: A review on the status of research activities in the past, the present and the future prospects. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2010;97:133–139. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2009.10.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

