SILK studies - capturing the turnover of proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 31222062
- PMCID: PMC6876864
- DOI: 10.1038/s41582-019-0222-0
SILK studies - capturing the turnover of proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
Alzheimer disease (AD) is one of several neurodegenerative diseases characterized by dysregulation, misfolding and accumulation of specific proteins in the CNS. The stable isotope labelling kinetics (SILK) technique is based on generating amino acids labelled with naturally occurring stable (that is, nonradioactive) isotopes of carbon and/or nitrogen. These labelled amino acids can then be incorporated into proteins, enabling rates of protein production and clearance to be determined in vivo and in vitro without the use of radioactive or chemical labels. Over the past decade, SILK studies have been used to determine the turnover of key pathogenic proteins amyloid-β (Aβ), tau and superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) in the cerebrospinal fluid of healthy individuals, patients with AD and those with other neurodegenerative diseases. These studies led to the identification of several factors that alter the production and/or clearance of these proteins, including age, sleep and disease-causing genetic mutations. SILK studies have also been used to measure Aβ turnover in blood and within brain tissue. SILK studies offer the potential to elucidate the mechanisms underlying various neurodegenerative disease mechanisms, including neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction, and to demonstrate target engagement of novel disease-modifying therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
H.Z. declares that he has served on scientific advisory boards for Roche Diagnostics, Samumed, CogRx and Wave and is one of the founders of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg, which is funded by GU Ventures (a Swedish government-owned company managed by the University of Gothenburg); these activities are all unrelated to this article. R.J.B. declares that he, along with Washington University, has an equity ownership interest in C2N Diagnostics (a mass-spectrometry-based biotechnology company that holds patents on the stable isotope labelling kinetics (SILK) technique in the United States and other countries) and receives royalties related to SILK and blood plasma assay technologies licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics. R.J.B. declares that he receives income from C2N Diagnostics for serving on its scientific advisory board. B.W.P. declares that he receives consultancy fees from C2N Diagnostics. T.M. and R.J.B. have licensed superoxide dismutase 1 SILK to C2N Diagnostics. N.C.W. holds a patent for SILK studies utilizing nanoscale secondary ion mass spectroscopy. K.Y. and T.W. declare that they are employed by C2N Diagnostics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

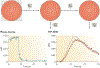

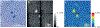
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

