Social skills training for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children aged 5 to 18 years
- PMID: 31222721
- PMCID: PMC6587063
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008223.pub3
Social skills training for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children aged 5 to 18 years
Abstract
Background: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children is associated with hyperactivity and impulsivity, attention problems, and difficulties with social interactions. Pharmacological treatment may alleviate the symptoms of ADHD but this rarely solves difficulties with social interactions. Children with ADHD may benefit from interventions designed to improve their social skills. We examined the benefits and harms of social skills training on social skills, emotional competencies, general behaviour, ADHD symptoms, performance in school of children with ADHD, and adverse events.
Objectives: To assess the beneficial and harmful effects of social skills training in children and adolescents with ADHD.
Search methods: In July 2018, we searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, 4 other databases and two trials registers.We also searched online conference abstracts, and contacted experts in the field for information about unpublished or ongoing randomised clinical trials. We did not limit our searches by language, year of publication, or type or status of publication, and we sought translation of the relevant sections of non-English language articles.
Selection criteria: Randomised clinical trials investigating social skills training versus either no intervention or waiting-list control, with or without pharmacological treatment of both comparison groups of children and adolescents with ADHD.
Data collection and analysis: We conducted the review in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention. We performed the analyses using Review Manager 5 software and Trial Sequential Analysis. We assessed bias according to domains for systematic errors. We assessed the certainty of the evidence with the GRADE approach.
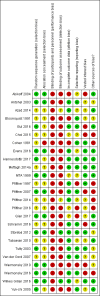
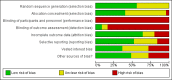
Main results: We included 25 randomised clinical trials described in 45 reports. The trials included a total of 2690 participants aged between five and 17 years. In 17 trials, participants were also diagnosed with various comorbidities.The social skills interventions were described as: 1) social skills training, 2) cognitive behavioural therapy, 3) multimodal behavioural/psychosocial therapy, 4) child life and attention skills treatment, 5) life skills training, 6) the "challenging horizon programme", 7) verbal self-instruction, 8) meta-cognitive training, 9) behavioural therapy, 10) behavioural and social skills treatment, and 11) psychosocial treatment. The control interventions were no intervention or waiting list.The duration of the interventions ranged from five weeks to two years. We considered the content of the social skills interventions to be comparable and based on a cognitive-behavioural model. Most of the trials compared child social skills training or parent training combined with medication versus medication alone. Some of the experimental interventions also included teacher consultations.More than half of the trials were at high risk of bias for generation of the allocation sequence and allocation concealment. No trial reported on blinding of participants and personnel. Most of the trials did not report on differences between groups in medication for comorbid disorders. We used all eligible trials in the meta-analyses, but downgraded the certainty of the evidence to low or very low.We found no clinically relevant treatment effect of social skills interventions on the primary outcome measures: teacher-rated social skills at end of treatment (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.11, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.00 to 0.22; 11 trials, 1271 participants; I2 = 0%; P = 0.05); teacher-rated emotional competencies at end of treatment (SMD -0.02, 95% CI -0.72 to 0.68; two trials, 129 participants; I2 = 74%; P = 0.96); or on teacher-rated general behaviour (SMD -0.06 (negative value better), 95% CI -0.19 to 0.06; eight trials, 1002 participants; I2 = 0%; P = 0.33). The effect on the primary outcome, teacher-rated social skills at end of treatment, corresponds to a MD of 1.22 points on the social skills rating system (SSRS) scale (95% CI 0.09 to 2.36). The minimal clinical relevant difference (10%) on the SSRS is 10.0 points (range 0 to 102 points on SSRS).We found evidence in favour of social skills training on teacher-rated core ADHD symptoms at end of treatment for all eligible trials (SMD -0.26, 95% CI -0.47 to -0.05; 14 trials, 1379 participants; I2= 69%; P = 0.02), but the finding is questionable due to lack of support from sensitivity analyses, high risk of bias, lack of clinical significance, high heterogeneity, and low certainty.The studies did not report any serious or non-serious adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: The review suggests that there is little evidence to support or refute social skills training for children and adolescents with ADHD. We may need more trials that are at low risk of bias and a sufficient number of participants to determine the efficacy of social skills training versus no training for ADHD. The evidence base regarding adolescents is especially weak.
Conflict of interest statement
Ole Jakob Storebø is an Associate Editor with the Cochrane Developmental, Psycosocial and Learning Problems Group. Mette Elmose Andersen ‐ none known Maria Skoog ‐ none known Signe Joost Hansen ‐ none known Erik Simonsen ‐ none known Nadia Pedersen ‐ none known Britta Tendal ‐ none known Henriette E Callesen ‐ none known Erlend G Faltinsen ‐ none known Christian Gluud ‐ none known
Ole Jakob Storebø, Maria Skoog, Erik Simonsen, and Christian Gluud were involved in the Storebø 2012 trial, which is included in this review. This trial was assessed by Nadia Pedersen, Mette Elmose, Signe Joost, and Mathilde Holmsov. These authors independently assessed the eligibility of this study, extracted data from it, assessed the risk of bias within it and assessed the quality of the evidence provided by it.
Figures





















Update of
-
Social skills training for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children aged 5 to 18 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;(12):CD008223. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008223.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 21;6:CD008223. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008223.pub3. PMID: 22161422 Updated.
Comment in
-
What are the effects of social skills training on children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? A Cochrane Review summary with commentary.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2021 Mar;63(3):250-251. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14786. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33368177 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abikoff 2004 {published data only}
-
- Abikoff H, Hectman L, Klein RG, Gallagher R, Fleiss K, Etcovitch J, et al. Social functioning in children with ADHD treated with long‐term methylphenidate and multimodal psychosocial treatment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2004;43(7):820‐9. [DOI: 10.1097/01.chi.0000128797.91601.1a; PUBMED: 15213583] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abikoff H, Hectman L, Klein RG, Weiss G, Fleiss K, Etcovitch J, et al. Symptomatic improvement in children with ADHD treated with long‐term methylphenidate and multimodal psychosocial treatment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2004;43(7):802‐11. [DOI: 10.1097/01.chi.0000128791.10014.ac; PUBMED: 15213581] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hechtman L, Abikoff H, Klein RG, Weiss G, Respitz C, Kouri J, et al. Academic achievement and emotional status of children with ADHD treated with long‐term methylphenidate and multimodal psychosocial treatment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2004;43(7):812‐9. [DOI: 10.1097/01.chi.0000128796.84202.eb; PUBMED: 15213582] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klein RG, Abikoff H, Hechtman L, Weiss G. Design and rationale of controlled study of long‐term methylphenidate and multimodal psychosocial treatment in children with ADHD. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2004;43(7):792‐801. [DOI: 10.1097/01.chi.0000128798.91601.fe; PUBMED: 15213580] - DOI - PubMed
Antshel 2003 {published data only}
Azad 2014 {published data only}
-
- Azad MA, Faramarzi S, Arefi M, Farhadi T, Fakkar A. The effectiveness of meta‐cognitive knowledge on reduced hyperactivity and improved attention in children afflicted with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in the primary school. Journal of Advances in Cognitive Science 2014;16(1):49‐57. [icssjournal.ir/article‐1‐223‐en.html]
Bloomquist 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bloomquist ML, August GJ, Ostrander R. Effects of a school‐based cognitive‐behavioral intervention for ADHD children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 1991;19(5):591‐605. [PUBMED: 1770187] - PubMed
-
- Bloomquist ML, Braswell L. Multicomponent cognitive‐behavior intervention for attention‐deficit hyperactivity disordered children. Data on file 1989.
Bul 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bul KC, Kato PM, Oord S, Danckaerts M, Vreeke LJ, Willems A, et al. Behavioral outcome effects of serious gaming as an adjunct to treatment for children with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2016;18(2):e26. [DOI: 10.2196/jmir.5173; PMC4773597; PUBMED: 26883052] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Choi 2015 {published data only}
Cohen 1981 {published data only}
-
- Cohen NJ, Sullivan J, Minde K, Novak C, Helwig C. Evaluation of the relative effectiveness of methylphenidate and cognitive behavior modification in the treatment of kindergarten‐aged hyperactive children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 1981;9(1):43‐54. [PUBMED: 7217537] - PubMed
Evans 2016 {published data only}
Hannesdottir 2017 {published data only}
Meftagh 2014a {published data only}
-
- Meftagh SD, Najimi A, Mohammadi N, Ghanizadeh A, Rahimi C, Amini MM. The most effective intervention for attention deficit‐hyperactivity disorder: using continuous performance test. Psychiatria Danubina 2014;26(2):165‐71. [PUBMED: 24909254] - PubMed
MTA 1999 {published data only}
-
- Arnold LE, Abikoff HB, Cantwell DP, Conners CK, Elliott GR, Greenhill LL, et al. NIMH collaborative multimodal treatment study of children with ADHD (MTA): design methodology, and protocol evolution. Journal of Attention Disorders 1997;2(3):141‐58. [DOI: 10.1177/108705479700200301] - DOI
-
- Arnold LE, Chuang S, Davies M, Abikoff HB, Conners CK, Elliot GR, et al. Nine months of multicomponent behavioral treatment for ADHD and effectiveness of MTA fading procedures. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 2004;32(1):39‐51. [PUBMED: 14998110] - PubMed
-
- Arnold LE, Elliot M, Sachs L, Bird H, Kraemer HC, Wells KC, et al. Effects of ethnicity on treatment attendance, stimulant response/dose, and 14‐month outcome in ADHD. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2003;71(4):713‐27. [PUBMED: 12924677] - PubMed
-
- Hinshaw SP, March JS, Abikoff H, Arnold LE, Cantwell DP, Conners CK, et al. Comprehensive assessment of childhood attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder in the context of a multisite, multimodal clinical trial. Journal of Attention Disorder 1997;1(4):217‐34. [DOI: 10.1177/108705479700100403] - DOI
Pfiffner 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pfiffner LJ, McBurnett K. Social skills training with parent generalization: treatment effects for children with attention deficit disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1997;65(5):749‐57. [PUBMED: 9337494] - PubMed
Pfiffner 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pfiffner LJ, Yee Mikami A, Huang‐Pollock C, Easterlin B, Zalecki C, McBurnett K. A randomized, controlled trial of integrated home‐school behavioral treatment for ADHD, predominantly inattentive type. Journal of American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2007;46(8):1041‐50. [DOI: 10.1097/chi.0b013e318064675f; PUBMED: 17667482] - DOI - PubMed
Pfiffner 2014 {published data only}
-
- Haack LM, Villodas M, McBurnett K, Hinshaw S, Pfiffner LJ. Parenting as a mechanism of change in psychosocial treatment for youth with ADHD, predominantly inattentive presentation. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 2017;45(5):841‐55. [DOI: 10.1007/s10802-016-0199-8; PMC5352559; PUBMED: 27628742] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pfiffner LJ, Hinshaw SP, Owens E, Zalecki C, Kaiser NM, Villodas M, et al. A two‐site randomized clinical trial of integrated psychosocial treatment for ADHD‐inattentive type. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2014;82(6):1115‐27. [DOI: 10.1037/a0036887; PMC4244306; PUBMED: 24865871] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Pfiffner 2016 {published data only}
-
- Pfiffner LJ, Rooney M, Haack L, Villodas M, Delucchi K, McBurnett K. A randomized controlled trial of a school‐implemented school‐home intervention for attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms and impairment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2016;55(9):762‐70. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jaac.2016.05.023; PUBMED: 27566117] - DOI - PubMed
Qian 2017 {published data only}
-
- Qian Y, Chen M, Shuai L, Cao QJ, Yang L, Wang YF. Effect of an ecological executive skill training program for school‐aged children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Chinese Medical Journal 2017;130(13):1513‐20. [DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.208236; PMC5494912; PUBMED: 28639564 ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Schramm 2016 {published data only}
-
- Schramm SA, Hennig T, Linderkamp F. Training problem solving and organizational skills in adolescents with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology 2016;15(3):391‐411. [DOI: 10.1891/1945-8959.15.3.391] - DOI
Storebø 2012 {published data only}
-
- Storebø OJ, Pedersen J, Skoog M, Thomsen PH, Winkel P, Gluud C, et al. Randomised social‐skills training and parental training plus standard treatment versus standard treatment of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ‐ the SOSTRA trial protocol. Trials 2011;12:18. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-18; PMC3038941; PUBMED: 21255399] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Storebø OJ, Skoog M, Rasmussen PD, Winkel P, Gluud C, Pedersen J, et al. Attachment competences in children with ADHD during the social‐skills training and attachment (SOSTRA) randomized clinical trial. Journal of Attention Disorders 2015;19(10):865‐71. [DOI: 10.1177/1087054713520220; PUBMED: 24532801] - DOI - PubMed
Tabaeian 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tabaeian SR, Kalantari M, Amiri S, Neshatdoost HT, Molavi H. Effectiveness of social skills training on social competence on primary school children with ADHD. Journal of Psychology 2010;13(4):362‐76.
Tutty 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tutty S, Gephart H, Wurzbacher K. Enhancing behavioral and social skill functioning in children newly diagnosed with attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder in a pediatric setting. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 2003;24(1):51‐7. [PUBMED: 12584485] - PubMed
Van der Oord 2007 {published data only}
-
- Oord S, Prins PJM, Oosterlaan J, Emmelkamp PMG. Does brief, clinically based, intensive multimodal behaviour therapy enhance the effects of methylphenidate in children with ADHD?. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2007;16(1):48‐57. [DOI: 10.1007/s00787-006-0574-z; PUBMED: 16972117] - DOI - PubMed
Waxmonsky 2010 {published data only}
-
- Waxmonsky JG, Waschbusch DA, Pelham WE, Draganac‐Cardona L, Rotella B, Ryan L. Effects of atomoxetine with and without behavior therapy on the school and home functioning of children with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2010;71(11):1535‐51. [DOI: 10.4088/JCP.09m05496pur; PUBMED: 20673557 ] - DOI - PubMed
Waxmonsky 2016 {published data only}
-
- Waxmonsky JG, Waschbusch DA, Belin P, Li T, Babocsai L, Humphery H, et al. A randomized clinical trial of an integrative group therapy for children with severe mood dysregulation. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2016;55(3):196‐207. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jaac.2015.12.011; PMC4764804; PUBMED: 26903253] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Wilkes Gillan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Wilkes‐Gillan S, Bundy A, Cordier R, Lincoln M, Chen YW. A randomised controlled trial of a play‐based intervention to improve the social play skills of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). PLOS One 2016;11(8):e0160558. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160558; PMC4987013; PUBMED: 27529693] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Yuk‐chi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yuk‐chi S. Effectiveness of Methylphenidate and Combined Treatment (Methylphenidate and Psychosocial Treatment) for Chinese Children with Attention‐Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in a Community Mental Health Center [PhD thesis]. Hong Kong (CN): The Chinese University of Hong Kong, 2005.
References to studies excluded from this review
Abikoff 2013 {published data only}
Bussing 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bussing R, Nelson MM, Kurtz S. Parent‐child interaction therapy: treatment components and evidence‐base. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2016;55(10 Suppl. 1):S351.
Cionek Szpak 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cionek‐Szpak E, Holtmann M, Stadler C, Poustka F. EEG‐Neurobiofeedback in ADHD ‐ a treatment supplement or alternative‐rapport about the results of a controlled experimental trial. Neuropsychiatrie de l'Enfance et de l'Adolescence 2012;60(5 Suppl. 1):s267.
Cipolla 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cipolla DS. An investigation of the effects of a computer‐based intervention on the social skills of children with autism. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences 2013;73(11‐A(E)):No pagination specified.
Corkum 2005 {published data only}
-
- Corkum PV, McKinnon MM, Mullane JC. The effect of involving classroom teachers in a parent training program for families of children with ADHD. Child & Family Behavior Therapy 2005;27(4):29‐49.
Dodge 2011 {published data only}
Döpfner 2004 {published data only}
-
- Döpfner M, Breuer D, Schürmann S, Metternich TW, Rademacher C, Lehmkuhl G. Effectiveness of an adaptive multimodal treatment in children with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder ‐ global outcome. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2004;13(Suppl. 1):117‐29. - PubMed
ESCAP 2013 {published data only}
-
- No authorship indicated. 15th International Congress of ESCAP ‐ European Society for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 2013 July 6‐10; Dublin (IRELAND). European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 2013;22(Suppl. 2):S81‐S323. - PubMed
Feinfield 2004 {published data only}
-
- Feinfield KA, Baker BL. Empirical support for a treatment program for families of young children with externalizing problems. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology 2004;33(1):182‐95. - PubMed
Gol 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gol D, Jarsus T. Effect of a social skills training group on everyday activities of children with attention deficit‐hyperactivity disorder. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2005;47(8):539‐45. - PubMed
Gonzalez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez LO, Sellers EW. The effects of a stress‐management program on self‐concept, locus of control, and the acquisition of coping skills in school‐age children diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing 2002;15(1):5‐15. - PubMed
Grasmann 2011 {published data only}
-
- Grasmann D, Stadler C. VIA ‐ an intensive therapeutic treatment program for conduct disorders [VIA ‐ intensivtherapeutischer behandlungsansatz bei storungen des sozialverhaltens]. Zeitschrift fur Kinder und Jugendpsychiatrie und Psychotherapie 2011;39(1):23‐31. - PubMed
Horn 1990 {published data only}
-
- Horn WF, Ialongo N, Greenberg G, Packard T, Smith‐Winberry C. Additive effects of behavioral parent training and self‐control therapy with attention deficit/ hyperactivity disordered children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology 1990;19(2):98‐110.
ICBM 2012 Meeting {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. ICBM 2012 Meeting. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine 2012;19(Suppl. 1):1‐342. - PubMed
Jans 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jans T, Jacob C, Hennighausen K, Roesler M, Haenig S, Sobanski E, et al. Treatment outcome of behavioral parent‐child training in childhood ADHD as a function of the treatment of maternal ADHD. Neuropsychiatrie de l'Enfance et de l'Adolescence 2012;60(Suppl. 5):S51.
Jans 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jans T, Jacob C, Warnke A, Zwanzger U, Groß‐Lesch S, Matthies S, et al. Does intensive multimodal treatment for maternal ADHD improve the efficacy of parent training for children with ADHD? A randomized controlled multicenter trial. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines 2015;56(12):1298‐313. - PubMed
Klein 1997 {published data only}
-
- Klein RG, Abikoff H. Behavior therapy and methylphenidate in the treatment of children with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders 1997;2(2):89‐114.
Kolko 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kolko DJ, Loar LL, Sturnick D. Inpatient social‐cognitive skills training groups with conduct disordered and attention deficit disordered children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 1990;31(5):737‐48. - PubMed
Kolko 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kolko DJ, Bukstein OG, Barron J. Methylphenidate and behavior modification in children with ADHD and comorbid ODD or CD: main and incremental effects across settings. Journal of American Academic Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 1999;38(5):578‐86. - PubMed
Langberg 2008 {published data only}
-
- Langberg JM, Epstein JN. Efficacy of an organization skills intervention to Improve the academic functioning of students with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. School Psychology Quarterly 2008;23(3):407‐17.
Langberg 2012 {published data only}
Lessard 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lessard L, Coutu S. Efficacy of a social skills program for children presenting with heterogeneous psychiatric diagnoses. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue Canadienne des Sciences du Comportement 2011;43(1):30‐9.
Leung 2017 {published data only}
-
- Leung C, Tsang S, Ng GSH, Choi SY. Efficacy of parent‐child interaction therapy with Chinese ADHD children: randomized controlled trial. Research on Social Work Practice 2017;27(1):36‐47.
Lim‐Ashworth 2013a {published data only}
-
- Lim‐Ashworth N, Ooi YP, Weng SJ, Lim CG, Fung DSS, Glenn A, et al. Preliminary findings on the effects of nutritional and social skills intervention among children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore 2013;42(9 Suppl. 1):S162.
Malti 2012 {published data only}
-
- Malti T, Ribeaud D, Eisner M. Effectiveness of a universal school‐based social competence program: the role of child characteristics and economic factors. International Journal of Conflict and Violence 2012;6(2):249‐59.
Miranda 2002 {published data only}
-
- Miranda A, Presentación J, Soriano M. Effectiveness of a school‐based multicomponent program for the treatment of children with ADHD. Journal of Learning Disabilities 2002;35(6):547‐63. - PubMed
Molina 2008 {published data only}
-
- Molina BSG, Flory K, Bukstein OG, Greiner AR, Baker JL, Krug V, et al. Feasibility and preliminary efficacy of an after‐school program for middle schoolers with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders 2008;12(3):207‐17. - PubMed
NCT02574273 {published data only}
-
- NCT02574273. Pilot trial of a social skills group treatment (Secret Agent Society Program). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02574273 (first received 12 October 2015).
NCT03176108 {published data only}
-
- NCT03176108. Evaluation of a parent/child cognitive‐behaviorial therapy program in ADHD children with emotional dysregulation profile. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03176108 (first received 5 June 2017).
Ostberg 2012 {published data only}
Pfiffner 2018 {published data only}
-
- Pfiffner LJ, Rooney ME, Jiang Y, Haack LM, Beaulieu A, McBurnett K. Sustained effects of collaborative school‐home intervention for Attention‐Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder symptoms and impairment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2018; Vol. 57, issue 4:245‐51. - PubMed
Power 2012a {published data only}
Pumpuang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pumpuang W, Phuphaibul R, Orathai P, Putdivarnichapong W. Effectiveness of a collaborative home‐school behavior management program for parents and teachers of children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Pacific RIM International Journal of Nursing Research 2012;16(2):138‐53.
Rosén 1984 {published data only}
-
- Rosén LA, O´Leary SG, Joyce AS, Conway G, Pfiffner L. The importance of prudent negative consequences for maintaining the appropriate behavior of hyperactive students. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 1984;12(4):581‐604. - PubMed
Sibley 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sibley MH, Pelham WE Jr, Derefinko KJ, Kuriyan AB, Sanchez F, Graziano PA. A pilot trial of Supporting Teens' Academic Needs Daily (STAND): a parent‐adolescent collaborative intervention for ADHD. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment 2013;35(4):436‐49.
Sibley 2013a {published data only}
-
- Sibley MH. Supporting Teens' Academic Needs Daily (STAND): a parent‐adolescent collaborative intervention for ADHD. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 2013;74(3‐B(E)):No pagination specified.
Sibley 2016 {published data only}
Vidal 2015 {published data only}
-
- Vidal R, Castells J, Richarte V, Palomar G, Garcia M, Nicolau R, et al. Group therapy for adolescents with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2015;54(4):275‐82. - PubMed
Wolraich 1978 {published data only}
-
- Wolraich M, Drummond T, Salomon MK, O´Brian ML, Sivage C. Effects of methylphenidate alone and in combination with behavior modification procedures on the behavior and academic performance of hyperactive children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 1978;6(1):149‐61. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
NCT01019252 {published data only}
-
- NCT01019252. Skills training for adolescents with ADHD [Compensatory executive functioning skills training in adolescents with ADHD]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01019252 (first received 20 November 2009).
References to ongoing studies
IRCT201609186834N11 {published data only}
-
- IRCT201609186834N11. The effect of psycho‐educational group therapy of emotional intelligence on enhancing of emotional intelligence of adolescents with ADHD. www.irct.ir (first received 30 October 2016).
NCT01330849 {published data only}
-
- NCT01330849. Toolkit for school behavior modification in children with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [A randomized controlled trial of a behavior modification toolkit in primary school children with ADHD behaviors]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01330849 (first received 5 April 2011).
NCT02937142 {published data only}
-
- NCT02937142. Cognitive behavior group therapy in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder [Cognitive behavior group therapy in adolescents (14‐18 years) with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02937142 (first received 14 October 2016).
Yang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yang L, Shuai L, Chen M, Qian Y, Wang Y. Efficacy of an integrated behavioural therapy for children with Attention‐Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: a randomized controlled trial. ADHD: Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders 2015;7(Suppl. 1):S94. [DOI: 10.1007/s12402-015-0169-y; P‐25‐0008] - DOI
Additional references
Abikoff 2011 [pers comm]
-
- Abikoff H. Cochrane review: social skills training [personal communication]. Email to: OJ Storebø 28 January 2011.
Achenbach 1991
-
- Achenbach TM. Integrative Guide for the 1991 CBCL/4‐18, YSR, and TRF Profiles. Burlington (VT): University of Vermont, Department of Psychology, 1991.
Almerie 2015
Andrews 2013a
-
- Andrews J, Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Alderson P, Dahm P, Falck‐Ytter Y, et al. GRADE guidelines: 14. Going from evidence to recommendations: the significance and presentation of recommendations. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(7):719‐25. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.03.013; PUBMED: 23312392] - DOI - PubMed
Andrews 2013b
-
- Andrews JC, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Pottie K, Meerpohl JJ, Coello PA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 15. Going from evidence to recommendation ‐ determinants of a recommendation's direction and strength. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(7):726‐35. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.02.003; PUBMED: 23570745] - DOI - PubMed
Antshel 2010 [pers comm]
-
- Antshel K. [personal communication]. Email to: OJ Storebø 16 December 2010.
Antshel 2011 [pers comm]
-
- Antshel K. [personal communication]. Email to: OJ Storebø 13 July 2011.
Attkisson 1982
-
- Attkisson CC, Zwick R. The client satisfaction questionnaire. Psychometric properties and correlations with service utilization and psychotherapy outcome. Evaluation and Program Planning 1982;5(3):233‐7. [PUBMED: 10259963] - PubMed
Balshem 2011
Barkley 1987
-
- Barkley RA. Defiant Children: A Clinician's Manual for Parent Training. 1st Edition. The Guilford Press, 1987.
Barkley 2002
-
- Barkely RA, Fischer M, Smallish L, Fletcher K. The persistence of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder into young adulthood as a function of reporting source and definition of disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 2002;111(2):279‐89. [PUBMED: 12003449] - PubMed
Berkley 1996
Brok 2008
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta‐analyses may be inconclusive ‐ trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta‐analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287‐98. [DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyn188; PUBMED: 18824466] - DOI - PubMed
Brunetti 2013
Castellanos 2006
Castellini 2018
Chan 2013
-
- Chan A‐W, Tetzlaff JM, Altman DG, Laupacis A, Gøtzsche PC, Krleža‐Jerić K, et al. SPIRIT 2013 statement: defining standard protocol items for clinical trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(3):200‐7. [DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-3-201302050-00583; PMC5114123; PUBMED: 23295957] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Chang 2012
Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group 2019
-
- Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. Information for authors. hbg.cochrane.org/information‐authors (accessed prior to 5 June 2019).
Conners 1998
-
- Conners KC, Sitarenios G, Parker JDA, Epstein JN. The Revised Conners´ Parent Rating Scale (CPRS‐R): factor structure, reliability, and criterion validity. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 1998;26(4):257‐68. [PUBMED: 9700518] - PubMed
Conners 2008a
-
- Conners KC. Conners Comprehensive Behavior Rating Scales (Conners CBRS). Toronto (ON): Multi‐Health Systems Inc, 2008.
Conners 2008b
-
- Conners KC. Conners 3. Toronto (ON): Multi‐Health Systems Inc, 2008.
Cortese 2016
Czamara 2013
-
- Czamara D, Tiesler CM, Kohlböck G, Berdel D, Hoffmann B, Bauer CP, et al. Children with ADHD symptoms have a higher risk for reading, spelling and math difficulties in the GINIplus and LISAplus cohort studies. PLOS ONE 2013;8(5):e63859. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063859; PMC3664565; PUBMED: 23724008] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Daley 2014b
-
- Daley D, Oord S, Ferrin M, Danckaerts M, Doepfner M, Cortese S, et al. Behavioral interventions in attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials across multiple outcome domains. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2014;53(8):835‐47. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jaac.2014.05.013; PUBMED: 25062591] - DOI - PubMed
Dalsgaard 2002
-
- Dalsgaard S, Mortensen PB, Frydenberg M, Thomsen PH. Conduct problems, gender and adult psychiatric outcome of children with attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry 2002;181(5):416‐21. [PUBMED: 12411268] - PubMed
Dalsgaard 2015
Dawson 2010
-
- Dawson P, Guare R. Executive Skills in Children and Adolescents: A Practical Guide to Assessment and Intervention. 2nd Edition. New York: The Guilford Press, 2010.
De Boo 2007
Donner 2002
DSM‐5
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐5). 5th Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
DSM‐III
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐III). 3rd Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
DSM‐IV
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV). 4th Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
DSM‐IV‐R
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐III‐R). 3rd Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
DSM‐IV‐TR
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV‐TR). 4th Edition. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Egger 1997
Elliot 1991
-
- Elliot SN, Gresham FM. Social Skills Intervention Guide: Practical Strategies for Social Skills Training. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service, 1991.
Erskine 2016
-
- Erskine HE, Norman RE, Ferrari AJ, Chan GC, Copeland WE, Whiteford HA, et al. Long‐term outcomes of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder and conduct disorder: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2016;55(10):841–50. [doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2016.06.016; PUBMED: 27663939] - PubMed
Eunethydis 2010
Evans 2017 [pers comm]
-
- Evans S. Questions regarding your study [personal communication]. Email to: J Signe 29 December 2017.
Faraone 2000
-
- Faraone SV, Biederman J, Spencer T, Wilens T, Seidman LJ, Mick E, et al. Attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: an overview. Biological Psychiatry 2000;48(1):9‐20. [PUBMED: 10913503] - PubMed
Fohlmann 2009a
-
- Fohlmann AH. Social skills training [Social færdighedstræning]. In: Nordentoft M, Melau M, Iversen T, Kjær S editor(s). Psychosis in Adolescents. Symptoms, Treatment and the Future [Psykose hos Unge. Symptomer, Behandling og Fremtid]. Copenhagen (DK): Psykiatrifondens Forlag, 2009:161‐89.
Fohlmann 2009b [pers comm]
-
- Storebø OJ. Social Skills Training [personal communication]. Email to: AH Fohlmann 10 April 2009.
Ford 2003
Franke 2012
Froehlich 2011
GRADE Working Group
-
- GRADE Working Group. GRADE. www.gradeworkinggroup.org (accessed 11 December 2018).
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University. GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed prior to 12 March 2018. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University, 2015.
Gresham 1990
-
- Gresham FM, Elliot SN. Social Skills Rating System. Circle Pines (MN): Assistance Service, 1990.
Guyatt 2011a
Guyatt 2011b
Guyatt 2011c
Guyatt 2011d
Guyatt 2011e
Guyatt 2011f
Guyatt 2011g
Guyatt 2013a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 11. Making an overall rating of confidence in effect estimates for a single outcome and for all outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):151–7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.006; PUBMED: 22542023] - DOI - PubMed
Guyatt 2013b
Guyatt 2013c
-
- Guyatt GH, Thorlund K, Oxman AD, Walter SD, Patrick D, Furukawa TA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 13. Preparing summary of findings tables and evidence profiles ‐ continuous outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):173–83. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.08.001; PUBMED: 23116689] - DOI - PubMed
Hannesdottir 2018 [pers comm]
-
- Hannesdottir D. [personal communication]. Email to: S Joost 18 January 2018.
Hannesdottir 2018b [pers comm]
-
- Hannesdottir D. [personal communication]. Email to: S Joost 9 February 2018.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
ICD‐10
-
- World Health Organization. The ICD‐10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders. Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines. Geneva (CH): World Health Organization, 1992.
ICD‐9
-
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases. 9th Edition. Vol. 1, Geneva (CH): World Health Organization, 1977.
ICH 1996
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. Guideline for Good Clinical Practice E6(R1). www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Efficacy/E... (accessed 6 May 2011).
International Congress on ADHD 2009
-
- International Congress on ADHD. 2nd International Congress on ADHD: from childhood to adult disease. www.adhd‐federation.org/fileadmin/user_upload/PDFs/ADHD_Final_Program.pdf (accessed prior to 29 May 2019).
Jakobsen 2014
-
- Jakobsen JC, Gluud C, Winkel P, Lange T, Wetterslev J. The thresholds for statistical and clinical significance – a five‐step procedure for evaluation of intervention effects in randomised clinical trials. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2014;14:34. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-34; PMC4015863; PUBMED: 24588900] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Kadesjö 2002
-
- Kadesjö B. ADHD in Children and Adults [ADHD hos Barn och Vuxna]. Stockholm (SE): Socialstyrelsen, 2002.
Kavale 1997
-
- Kavale KA, Mathur SR, Forness SR, Rutherford Jr RB, Quinn MM. Effectiveness of social skills training for students with behaviour disorders: a meta‐analysis. Advances in Learning and Behavioral Disabilities 1997;11:1‐26.
Kendal 1982
-
- Kendall PC, Braswell L. Cognitive‐behavioral self‐control therapy for children: a components analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1982;50:672‐90. - PubMed
Keshavan 2003
-
- Keshavan MS, Sujata M, Mehra A, Montrose DM, Sweeney JA. Psychosis proneness and ADHD in young relatives of schizophrenia patients. Schizophrenia Research 2003;59(1):85‐92. [12413647] - PubMed
Keus 2010
Kjaergard 2002
-
- Kjaergard LL, Gluud C. Citation bias of hepato‐biliary randomized clinical trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2002;55(4):407‐10. [PUBMED: 11927210] - PubMed
Koisaari 2015
-
- Koisaari T, Michelsson K, Holopainen JM, Maksimainen R, Päivänsalo J, Rantala K, et al. Traffic and criminal behavior of adults with attention deficit‐hyperactivity with a prospective follow‐up from birth to the age of 40 years. Traffic Injury Prevention 2015;16(8):824‐30. [DOI: 10.1080/15389588.2015.1029068; PUBMED: 25837647] - DOI - PubMed
Kwak 2002
-
- Kwak K, Park H, Kim C. The Manual for the Korean WISC‐III. Seoul: Special Education Publishing Co, 2002.
Landau 1991
-
- Landau S, Moore LA. Social skill deficits in children with attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder. School Psychology Review 1991;20(2):235‐51.
Lau 1995
Lauth 2004
-
- Lauth GW, Fellner C. Course of therapy and long‐term effects of a multimodal therapy program in ADHD. Single case studies [Therapieverlauf und langzeiteffekt eines multimodalen trainingsprogramms bei Aufmerksamkeitsdefizit‐/Hyperaktivitätsstörungen. Einzelfallstudien]. Kindheit und Entwicklung 2004;13(3):167‐79. [DOI: 10.1026/0942-5403.13.3.167] - DOI
Liberman 1988
-
- Liberman RP. Social skills training. In: Liberman RP editor(s). Psychiatric Rehabilitation of Chronic Mental Patients. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Press, 1988.
Mager 2005
Majewicz‐Hefley 2007
Meichenbaum 1978
-
- Meichenbaum D. Cognitive‐Behavior Modification: An Integrative Approach. New York (NY): Plenum Press, 1978.
Moher 2009
Mustafa 2013
-
- Mustafa RA, Santesso N, Brozek J, Akl EA, Walter SD, Norman G, et al. The GRADE approach is reproducible in assessing the quality of evidence of quantitative evidence syntheses. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(7):736‐42. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.02.004; PUBMED: 23623694] - DOI - PubMed
Nakao 1994
-
- Nakao K, Treas J. Updating occupational prestige and socioeconomic scores: how the new measures measure up. Sociological Methodology 1994;24:1‐72. [DOI: 10.2307/270978] - DOI
Neale 2010
-
- Neale BM, Medland SE, Ripke S, Asherson P, Franke B, Lesch KP, et al. Meta‐analysis of genome‐wide association studies of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2010;49(9):884‐97. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jaac.2010.06.008; PMC2928252; PUBMED: 20732625] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Newcorn 2008
NICE 2009
-
- National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health, commissioned by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management of ADHD in Children, Young People and Adults. National Clinical Practice Guideline Number 72. Leicester and London: The British Psychological Society and The Royal College of Psychiatrists, 2009. - PubMed
NICE 2018
-
- NICE. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: diagnosis and management. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng87/resources/attention‐deficit‐hyperactivity‐... (accessed 12 July 2018).
Nigg 2005
Nordic ADHD konference 2010
-
- Nordic ADHD konference 2010. Nordic ADHD conference: lifelong perspectives of special needs [Nordic ADHD konference: livslange perspektiver of specielle behov]. www.bupnet.dk/media/ADHD‐konference_maj_2010‐_Program%5B1%5D.pdf (accessed prior to 29 May 2019).
Norman 2003
Pasini 2007
Pelham 1992
Perroud 2014
-
- Perroud N, Cordera P, Zimmermann J, Michalopoulos G, Bancila V, Prada P, et al. Comorbidity between attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and bipolar disorder in a specialized mood disorders outpatient clinic. Journal of Affective Disorders 2014;168:161‐6. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.06.053; PUBMED: 25051093] - DOI - PubMed
Pfiffner 2011 [pers comm]
-
- Pfiffner L. Cochrane review: Social skills training [personal communication]. Email to: OJ Storebø 26 May 2011.
Pfiffner 2011b [pers comm]
-
- Pfiffner L. Cochrane review: Social skills training [personal communication]. Email to: OJ Storebø 25 May 2011.
Pineda 2003
-
- Pineda DA, Lopera F, Palacio JD, Ramirez D, Henao GC. Prevalence estimations of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: differential diagnoses and comorbidities in a Columbian sample. International Journal of Neuroscience 2003;113(1):49‐71. [PUBMED: 12691001] - PubMed
Polanczyk 2007
Punja 2016
-
- Punja S, Shamseer L, Hartling L, Urichuk L, Vandermeer B, Nikles J, et al. Amphetamines for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009996.pub2; PUBMED: 26844979] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Savovic 2018
-
- Savović J, Turner RM, Mawdsley D, Jones HE, Beynon R, Higgins JPT, et al. Association between risk‐of‐bias assessments and results of randomized trials in Cochrane Reviews: the ROBES Meta‐Epidemiologic Study. American Journal of Epidemiology 2018;187(5):1113‐22. [DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwx344; PMC5928453; PUBMED: 29126260] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Savovíc 2012
-
- Savović S, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157(6):429–38. [DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-6-201209180-00537; PUBMED: 22945832] - DOI - PubMed
Schachar 1997
Schmidt 2009
Schultz 1995
-
- Schultz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. [PUBMED: 7823387] - PubMed
Schulz 2010
Sergeant 2003
-
- Sergeant JA, Geurts H, Huijbregts S, Scheres A, Oosterlaan J. The top and the bottom of ADHD: a neuropsychological perspective. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 2003;27(7):583‐92. [PUBMED: 14624803] - PubMed
Storebø 2014
Storebø 2015
Storebø 2018
-
- Storebø OJ, Pedersen N, Ramstad E, Kielsholm ML, Nielsen SS, Krogh HB, et al. Methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents – assessment of adverse events in non‐randomised studies.. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 5. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012069.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Swanson 2007
-
- Swanson JM, Hinshaw SP, Arnold LE, Gibbons RD, Marcus S, Hur K, et al. Secondary evaluations of MTA 36‐month outcomes: propensity score and growth mixture model analyses. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2007;46(8):1003‐14. [DOI: 10.1097/CHI.0b013e3180686d63; PUBMED: 17667479] - DOI - PubMed
Thalheimer 2002
-
- Thalheimer W, Cook S. How to calculate effect sizes from published research articles: a simplified methodology. www.bwgriffin.com/gsu/courses/edur9131/content/Effect_Sizes_pdf5.pdf (accessed 28 May 2011).
Thomas 2015
Thorlund 2009
Thorlund 2011
-
- Thorlund K, Walter SD, Johnston BC, Furukawa TA, Guyatt GH. Pooling health‐related quality of life outcomes in meta‐analysis ‐ a tutorial and review of methods for enhancing interpretability. Research Synthesis Methods 2011;2:188‐203. - PubMed
US FDA 2011
-
- US Food, Drug Administration. Communication about an ongoing safety review of stimulant medications used in children with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsa... (accessed 6 May 2011).
Van der Oord 2008
Van Eck 2010
-
- Eck K, Finney JS, Evans S. Parent report of ADHD symptoms of early adolescents: a confirmatory factor analysis of the Disruptive Behavior Disorders scale. Educational and Psychological Measurement 2010;70:1042‐59.
Walcott 2004
Waschbusch 2011 [pers comm]
-
- Waschbusch D. Cochrane review: Social skills training [personal communication]. Email to: OJ Storebø 22 June 2011.
Wechsler 2003
-
- Wechsler D. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children. 4th Edition. London (UK): Pearson, 2003.
Weller 2010
-
- Weller EB, Weller RA, Fristad MA, Rooney MT, Schecter BA. Children's Interview for Psychiatric Syndromes (ChIPS). Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 2000;39(1):76‐84. - PubMed
Wetterslev 2008
Wetterslev 2009
Wetterslev 2017
Whalen 1985
-
- Whalen CK, Henker B. The social worlds of hyperactive (ADHD) children. Clinical Psychology Review 1985;5(5):447‐78. [DOI: 10.1016/0272-7358(85)90004-2] - DOI
Willcut 2012
Willis 2019
Wolraich 2007
Wood 2008
-
- Wood L, Egger M, Gluud LL, Schultz KF, Jüni P, Altman DG, et al. Empirical evidence of bias in treatment effect estimates in controlled trials with different interventions and outcomes: meta‐epidemiological study. BMJ 2008;336(7644):601‐5. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39465.451748.AD; PMC2267990; PUBMED: 18316340] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
World Congress on ADHD 2011
-
- World Congress on ADHD. 3rd World Congress on ADHD: from childhood to adult disease. ADHD Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders 2011;3(2):77‐234. [DOI: 10.1007/s12402-011-0058-y] - DOI
World Congress on ADHD 2013
-
- World Congress on ADHD. 4th World Congress on ADHD: from childhood to adult disease. ADHD Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders 2013;5(2):111‐247. [DOI: 10.1007/s12402-013-0109-7] - DOI
World Congress on ADHD 2015
World Congress on ADHD 2017
-
- World Congress on ADHD. 6th World Congress on ADHD: from child to adult disorder. ADHD Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders 2017;9(Suppl. 1):S1‐S55. [10.1007/s12402‐017‐0224‐y] - PubMed
Xu 2018
Yoshimasu 2012
-
- Yoshimasu K, Barbaresi WJ, Colligan RC, Voigt RG, Killian JM, Weaver AL, et al. Childhood ADHD is strongly associated with a broad range of psychiatric disorders during adolescence: a population‐based birth cohort study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines 2012;53(10):1036‐43. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2012.02567.x; PMC3608464; PUBMED: 22647074] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Storebø 2010
Storebø 2011
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

