Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: Role of tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 31222971
- PMCID: PMC6712467
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2327
Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: Role of tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
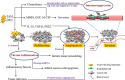
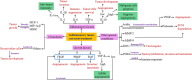
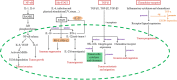
Tumor microenvironment is a complex system that contains multiple cells and cytokines. Among the multiple immune cells, macrophage is particularly abundant and plays an important role throughout the tumor progression process, namely, tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) in this special tumor microenvironment. Many kinds of cytokines from TAMs and other immune cells in tumor niche are involved in the linkage of inflammation, immunity and tumorigenesis. Inflammatory responses induced by TAMs are crucial to tumor development of different stages. This review highlights the critical role of TAMs in the linkage of inflammation, immunity, and cancer. It outlines the molecules of inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors mainly from TAMs in tumor microenvironment and their functions in tumor development during the major issues of angiogenesis, chronic inflammation, and immune suppression. Additionally, the signaling pathways involved in tumor progression and the crosstalk between them are also summarized.
Keywords: TAMs; angiogenesis; chronic inflammation; immune suppression; tumor.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Luster AD, Alon R, von Andrian UH. Immune cell migration in inflammation: present and future therapeutic targets. International Congress. 2005;1271:135‐138. - PubMed
-
- Woo SR, Corrales L, Gajewski TF. Innate immune recognition of cancer. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:445‐474. - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi K, Karin M. NF‐κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:309‐324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

