Antibacterial Activity study of Musizin isolated from Rhamnus wightii Wight and Arn
- PMID: 31223211
- PMCID: PMC6563663
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630014511
Antibacterial Activity study of Musizin isolated from Rhamnus wightii Wight and Arn
Abstract
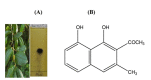
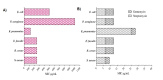
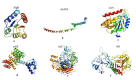
The crude extracts and the compounds isolated from traditional medicinal plants are used to treat infectious diseases caused by bacteria, fungi, and viruses. An attempt has been made in the present investigation to evaluate the antibacterial activity of musizin isolated from Rhamnus wightii, (Family: Rhamnaceae) against Gram-positive (Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus faecalis), and Gramnegative (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacteria. The tested compound showed more pronounced antibacterial activity against the tested pathogens than the standard antibiotics like streptomycin and gentamycin with the lowest minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Molecular docking analysis was performed to study the effectiveness of musizin compared to the standard antibiotics; it showed a significant interaction with the target proteins such asalgR (P. arginosa), divIVA (E. faecalis), icaA (S. aureus), plcR(B. cereus), treC (K. pneumonia) and ftsl (E. coli) and found that musizin showed higher potential with least binding energy. It has also been found that musizin had better ADMET properties than the standard drugs. Thus,musizin acts as an inhibitor of bacterial growth for consideration as a drug to treat bacterial infections.
Keywords: Musizin; Rhamnus wightii; antibacterial activity; in silico analysis; target receptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activity of native California medicinal plant extracts isolated from Rhamnus californica and Umbellularia californica.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2015 May 23;14:29. doi: 10.1186/s12941-015-0086-0. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2015. PMID: 26001558 Free PMC article.
-
The antibacterial activity of extracts of nine plant species with good activity against Escherichia coli against five other bacteria and cytotoxicity of extracts.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Feb 28;17(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1645-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28241818 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for antimicrobial activity of ten medicinal plants used in Colombian folkloric medicine: a possible alternative in the treatment of non-nosocomial infections.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2006 Feb 17;6:2. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-6-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2006. PMID: 16483385 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial and anti-Quorum Sensing activities of selected medicinal plants of Ethiopia: Implication for development of potent antimicrobial agents.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Jul 11;16(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0765-9. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27400878 Free PMC article.
-
Sulopenem: An Intravenous and Oral Penem for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Drugs. 2022 Apr;82(5):533-557. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01688-1. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35294769 Review.
Cited by
-
Hierarchical Assembly of Nanodimensional Silver-Silver Oxide Physical Gels Controlling Nosocomial Infections.ACS Omega. 2020 Dec 9;5(50):32617-32631. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04957. eCollection 2020 Dec 22. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33376899 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
