Analytical evaluation of the new Seal Autoanalyzer 3 High Resolution for urinary iodine determination
- PMID: 31223253
- PMCID: PMC6559621
- DOI: 10.11613/BM.2019.020711
Analytical evaluation of the new Seal Autoanalyzer 3 High Resolution for urinary iodine determination
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Analytical evaluation of the new Seal Autoanalyzer 3 High Resolution for urinary iodine determination.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2019 Oct 15;29(3):031201. doi: 10.11613/BM.2019.031201. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2019. PMID: 31624466 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the study was to evaluate the analytical performance of the new colorimetric, automatic analyser, Seal AutoAnalyzer 3 High Resolution (Seal AA3 HR) (Seal Analytical, Wisconsin, USA) for urinary iodine measurement.
Materials and methods: This study included testing of several analytical features of the method involving: imprecision (within-run %CVr, between-run %CVb and total laboratory precision %CVl), measurement uncertainty, carryover, linearity and method comparison, with 70 urine samples including the measuring range (20 - 700 µg/L).
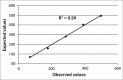
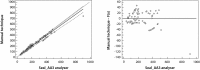
Results: Within-run, %CVb and %CVl of two control levels were 2.03% and 3.04%, 0.51% and 2.61%, and 2.09% and 4.01%, respectively. Carryover effect was less than 1%. The linearity was good in the range of urinary iodine values between 60 and 500 µg/L (R2 = 0.99). Good agreement of urinary iodine values was found between manual technique and Seal AA3 HR, using Passing-Bablok regression (y = 7.84 (- 3.00 to 15.29) + 0.95 (0.90 to 1.00) x) and Blant-Altman test. Cusum test for linearity indicates that there is no significant deviation from linearity (P > 0.1).
Conclusions: The obtained results proved excellent precision, reproducibility and linearity, comparable to the already used, manual method. The New Seal AA3 HR automatic analyser is acceptable for urinary iodine measurement with very good analytical characteristics and can be used for urinary iodine epidemiological studies of the Croatian population.
Keywords: colorimetry; iodine; method evaluation; urine.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Iodine status worldwide: WHO global database on iodine deficiency. Geneva: WHO; 2004. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2004/9241592001.pdf. Accessed February 14th 2019.
-
- Eastman CJ, Zimmermann MB. The Iodine Deficiency Disorders. [Updated 2018 Feb 6]. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al., eds. Endotext [Internet]. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK285556/. Accessed February 12th 2019.
-
- Laurberg P, Pedersen IB, Carlé AS, editors. The U-Shaped Curve of Iodine Intake and Thyroid Disorders. In: Comprehensive Handbook of Iodine. Preedy VR, Burrow GN, Watson R, eds. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780123741356/comprehensivehandbook-o.... Accessed August 15th 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-374135-6.00047-9 - DOI

