Filaggrin and atopic march
- PMID: 31223255
- PMCID: PMC6559618
- DOI: 10.11613/BM.2019.020501
Filaggrin and atopic march
Abstract
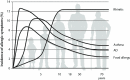
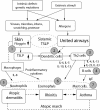
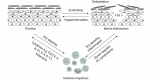
There is an increasing number of experimental, genetic and clinical evidence of atopic dermatitis expression as a pre-condition for later development of other atopic diseases such as asthma, food allergy and allergic rhinitis. Atopic dermatitis is a heterogeneous, recurrent childhood disease, also present in the adult age. It is increasingly attributed to systemic features and is characterized by immunological and skin barrier integrity and function dysregulation. To maintain the protective function of the skin barrier, in particular the maintenance of pH, hydration and antimicrobial functions, the filaggrin, among others, plays a significant role. Filaggrin is a multifunctional, histidine-rich, insoluble protein. The lack of filaggrin is associated with various cutaneous (e.g. ichthyosis vulgaris, allergic contact dermatitis) and non-cutaneous (e.g. diabetes, inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract) diseases and may be a result of genetic, immunological factors combined with environmental factors. In this review we summarised (emphasized) recent findings in understanding the role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and other diseases, participants in the atopic march.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; atopic diseases; filaggrin.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atopic March in a Case of Filaggrin Gene Mutation.Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol. 2025 Jun;38(2):61-64. doi: 10.1089/ped.2024.0118. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol. 2025. PMID: 40197870
-
The role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations in atopic dermatitis.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Oct;8(5):406-10. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32830e6fb2. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18769192 Review.
-
Revisiting the Roles of Filaggrin in Atopic Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 10;23(10):5318. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105318. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breaking the (un)sound barrier: filaggrin is a major gene for atopic dermatitis.J Invest Dermatol. 2006 Jun;126(6):1200-2. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700365. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16702964
-
Loss-of-function mutations within the filaggrin gene and atopic dermatitis.Curr Probl Dermatol. 2011;41:35-46. doi: 10.1159/000323291. Epub 2011 May 12. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21576945 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effects of α-Boswellic Acid on Tnf-α/Ifn-γ-Stimulated HaCat Cells and DNCB-Induced BALB/c Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 30;23(17):9863. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179863. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077254 Free PMC article.
-
Ichthyosis vulgaris: An updated review.Skin Health Dis. 2022 Nov 25;3(1):e187. doi: 10.1002/ski2.187. eCollection 2023 Feb. Skin Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36751330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trichohyalin gene expression is negatively correlated with the severity of dermatitis in a canine atopic dermatitis model.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Aug 21;11:1396557. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1396557. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39234173 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Inflammatory Chronic Skin Diseases.Cells. 2021 Dec 16;10(12):3559. doi: 10.3390/cells10123559. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filaggrin-Associated Atopic Skin, Eye, Airways, and Gut Disease, Modifying the Presentation of X-Linked Reticular Pigmentary Disorder (XLPDR).J Clin Immunol. 2024 Jan 2;44(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01637-x. J Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38165470
References
-
- Coca AF, Cooke RA. On the classification of the phenomena of hypersensitiveness. J Immunol. 1923;8:163–82.
-
- Salazar- Espinoza JF The atopic march. A Literature Review. Int J Med Students. 2014;2:119–24.

