Post-analytical laboratory work: national recommendations from the Working Group for Post-analytics on behalf of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
- PMID: 31223256
- PMCID: PMC6559616
- DOI: 10.11613/BM.2019.020502
Post-analytical laboratory work: national recommendations from the Working Group for Post-analytics on behalf of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Abstract
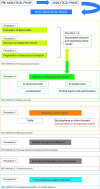
The post-analytical phase is the final phase of the total testing process and involves evaluation of laboratory test results; release of test results in a timely manner to appropriate individuals, particularly critical results; and modification, annotation or revocation of results as necessary to support clinical decision-making. Here we present a series of recommendations for post-analytical best practices, tailored to medical biochemistry laboratories in Croatia, which are intended to ensure alignment with national and international norms and guidelines. Implementation of the national recommendations is illustrated through several examples.
Keywords: clinical laboratory; harmonization; post-analytical phase; recommendations; test report.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Policies and practices in haemostasis testing among laboratories in Croatia: a survey on behalf of a Working Group for Laboratory Coagulation of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017 Feb 15;27(1):199-216. doi: 10.11613/BM.2017.022. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017. PMID: 28392741 Free PMC article.
-
General position of Croatian medical biochemistry laboratories on autovalidation: survey of the Working Group for Post-analytics of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020 Jun 15;30(2):020702. doi: 10.11613/BM.2020.020702. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020. PMID: 32292280 Free PMC article.
-
Capillary blood sampling: national recommendations on behalf of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2015 Oct 15;25(3):335-58. doi: 10.11613/BM.2015.034. eCollection 2015. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2015. PMID: 26524965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
External quality assessment of medical laboratories in Croatia: preliminary evaluation of post-analytical laboratory testing.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017 Feb 15;27(1):144-152. doi: 10.11613/BM.2017.018. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017. PMID: 28392737 Free PMC article.
-
External Quality Assessment in Croatia: problems, challenges, and specific circumstances.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017 Feb 15;27(1):86-92. doi: 10.11613/BM.2017.011. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017. PMID: 28392730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishing paediatric reference intervals for thyroid function tests in Croatian population on the Abbott Architect i2000.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021 Oct 15;31(3):030702. doi: 10.11613/BM.2021.030702. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021. PMID: 34393595 Free PMC article.
-
Errors within the total laboratory testing process, from test selection to medical decision-making - A review of causes, consequences, surveillance and solutions.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020 Jun 15;30(2):020502. doi: 10.11613/BM.2020.020502. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020. PMID: 32550813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
National Guidelines for the Performance of the Sweat Test in Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis on behalf of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine and the Cystic Fibrosis Centre - Paediatrics and adults, University Hospital Centre Zagreb.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2022 Feb 15;32(1):010501. doi: 10.11613/BM.2022.010501. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2022. PMID: 35210925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of continuous quality improvement of tuberculosis and HIV diagnostic services in Amhara Public Health Institute, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 19;15(3):e0230532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230532. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32191762 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Evaluation of Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) Devices: Insights From a Tertiary Care Hospital.Cureus. 2025 Mar 12;17(3):e80499. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80499. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40225426 Free PMC article.