Elevated activated partial thromboplastin time-based clot waveform analysis markers have strong positive association with acute venous thromboembolism
- PMID: 31223264
- PMCID: PMC6559615
- DOI: 10.11613/BM.2019.020710
Elevated activated partial thromboplastin time-based clot waveform analysis markers have strong positive association with acute venous thromboembolism
Abstract
Introduction: A hypercoagulable state is a predisposition for venous thromboembolism (VTE). The activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)-based clot waveform analysis (CWA) is a global haemostatic measure but its role in assessment of hypercoagulability and thrombotic disorders is uncertain. We aimed to study the changes of CWA parameters in acute VTE. We hypothesized that patients with acute VTE would demonstrate higher CWA values than control patients without VTE and having elevated CWA parameters is associated with acute VTE.
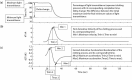
Materials and methods: Clot waveform analysis data from patients (N = 45) with objectively proven acute VTE who had an aPTT performed prior to initiation of anticoagulation were compared with controls (N = 111). The CWA parameters measured were min1, min2, max2 and delta change.
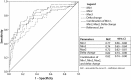
Results: While the mean aPTT between VTE patients and controls did not differ (P = 0.830), the mean CWA parameters were significantly higher among VTE patients than controls (min1, P < 0.001; min2, P = 0.001; max2, P = 0.002; delta change, P < 0.001). There were significantly more cases within the VTE group exhibiting CWA values above their reference intervals than the control group (all P < 0.001), with the odds ratios for VTE of 8.0, 5.2, 4.8 and 18.6 for min1, min2, max2 and delta change, respectively (all P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Patients with acute VTE had elevated aPTT-based CWA parameters than controls. Higher CWA parameters were significantly associated with acute VTE.
Keywords: activated partial thromboplastin time; blood coagulation; thrombophilia; thrombosis; venous thromboembolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated partial thromboplastin time-based clot waveform analysis: a potential for application in acute myocardial infarction and its complications.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 9;14(1):20917. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60098-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39251656 Free PMC article.
-
A correlation of thrombin generation assay and clot waveform analysis in patients on warfarin.Hematology. 2022 Dec;27(1):337-342. doi: 10.1080/16078454.2022.2043573. Hematology. 2022. PMID: 35255239
-
Assessment of aPTT-based clot waveform analysis for the detection of haemostatic changes in different types of infections.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 25;10(1):14186. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71063-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32843693 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Application of Clot Waveform Analysis.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025 Jan-Dec;31:10760296251331606. doi: 10.1177/10760296251331606. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025. PMID: 40170405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clot Waveform Analysis for Hemostatic Abnormalities.Ann Lab Med. 2023 Nov 1;43(6):531-538. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.6.531. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Ann Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 37387486 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and laboratory features of hypercoagulability in COVID-19 and other respiratory viral infections amongst predominantly younger adults with few comorbidities.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 19;11(1):1793. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81166-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33469056 Free PMC article.
-
In Reply: Dismantling the Apocalypse Narrative: The Myth of the COVID-19 Stroke.Neurosurgery. 2021 Feb 16;88(3):E277-E280. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyaa522. Neurosurgery. 2021. PMID: 33370813 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 associated coagulopathy in critically ill patients: A hypercoagulable state demonstrated by parameters of haemostasis and clot waveform analysis.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 Apr;51(3):663-674. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02318-x. Epub 2020 Oct 24. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 33098540 Free PMC article.
-
HYPERTENSION AND DIABETES MELLITUS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH DEEP VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: A CASE CONTROL STUDY.Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2024 Apr 30;22(1):34-38. Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2024. PMID: 38939895 Free PMC article.
-
Reagent Effects on the Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time Clot Waveform Analysis: A Multi-Centre Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 22;13(14):2447. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142447. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Hylckama Vlieg A, van der Linden IK, Bertina RM, Rosendaal FR. High levels of factor IX increase the risk of venous thrombosis. Blood. 2000;95:3678–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

