Aplnra/b Sequentially Regulate Organ Left-Right Patterning via Distinct Mechanisms
- PMID: 31223282
- PMCID: PMC6567806
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.30100
Aplnra/b Sequentially Regulate Organ Left-Right Patterning via Distinct Mechanisms
Abstract
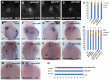
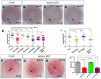
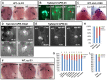
The G protein-coupled receptor APJ/Aplnr has been widely reported to be involved in heart and vascular development and disease, but whether it contributes to organ left-right patterning is largely unknown. Here, we show that in zebrafish, aplnra/b coordinates organ LR patterning in an apela/apln ligand-dependent manner using distinct mechanisms at different stages. During gastrulation and early somitogenesis, aplnra/b loss of function results in heart and liver LR asymmetry defects, accompanied by disturbed KV/cilia morphogenesis and disrupted left-sided Nodal/spaw expression in the LPM. In this process, only aplnra loss of function results in KV/cilia morphogenesis defect. In addition, only apela works as the early endogenous ligand to regulate KV morphogenesis, which then contributes to left-sided Nodal/spaw expression and subsequent organ LR patterning. The aplnra-apela cascade regulates KV morphogenesis by enhancing the expression of foxj1a, but not fgf8 or dnh9, during KV development. At the late somite stage, both aplnra and aplnrb contribute to the expression of lft1 in the trunk midline but do not regulate KV formation, and this role is possibly mediated by both endogenous ligands, apela and apln. In conclusion, our study is the first to identify a role for aplnra/b and their endogenous ligands apela/apln in LR patterning, and it clarifies the distinct roles of aplnra-apela and aplnra/b-apela/apln in orchestrating organ LR patterning.
Keywords: apela/apln; aplnra/b; left right patterning; midline; spaw.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cdon is essential for organ left-right patterning by regulating dorsal forerunner cells clustering and Kupffer's vesicle morphogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 22;12:1429782. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1429782. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39239564 Free PMC article.
-
Klf8 regulates left-right asymmetric patterning through modulation of Kupffer's vesicle morphogenesis and spaw expression.J Biomed Sci. 2017 Jul 17;24(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12929-017-0351-y. J Biomed Sci. 2017. PMID: 28716076 Free PMC article.
-
Dvr1 transfers left-right asymmetric signals from Kupffer's vesicle to lateral plate mesoderm in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2013 Oct 1;382(1):198-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23791819 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct mechanisms determine organ left-right asymmetry patterning in an uncoupled way.Bioessays. 2014 Mar;36(3):293-304. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300128. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 24464475 Review.
-
Apelin and Elabela/Toddler; double ligands for APJ/Apelin receptor in heart development, physiology, and pathology.Peptides. 2019 Jan;111:62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.04.011. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Peptides. 2019. PMID: 29684595 Review.
Cited by
-
Apela promotes blood vessel regeneration and remodeling in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 14;14(1):3718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50677-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38355946 Free PMC article.
-
Cxcr4a regulates heart progenitor development and cardiac rhythm in zebrafish.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Jul 13;39:101782. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101782. eCollection 2024 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39108621 Free PMC article.
-
Cdon is essential for organ left-right patterning by regulating dorsal forerunner cells clustering and Kupffer's vesicle morphogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 22;12:1429782. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1429782. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39239564 Free PMC article.
-
Mcm5 Represses Endodermal Migration through Cxcr4a-itgb1b Cascade Instead of Cell Cycle Control.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 10;12(2):286. doi: 10.3390/biom12020286. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204787 Free PMC article.
-
Mild cold stress specifically disturbs clustering movement of DFCs and sequential organ left-right patterning in zebrafish.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 23;10:952844. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.952844. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36211472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Dowd BF, Heiber M, Chan A. et al. A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene. 1993;136:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y. et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;251:471–476. - PubMed
-
- Farkasfalvi K, Stagg MA, Coppen SR. et al. Direct effects of apelin on cardiomyocyte contractility and electrophysiology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;357:889–895. - PubMed
-
- Kuba K, Zhang L, Imai Y. et al. Impaired heart contractility in Apelin gene-deficient mice associated with aging and pressure overload. Circ Res. 2007;101:e32–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

