Clinical value of detecting IQGAP3, B7-H4 and cyclooxygenase-2 in the diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 31223291
- PMCID: PMC6570966
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-0881-3
Clinical value of detecting IQGAP3, B7-H4 and cyclooxygenase-2 in the diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: The IQ-motif-containing GTPase-activating protein (IQGAP) family comprises three members, IQGAP1, IQGAP2 and IQGAP3. IQGAP3 is the latest addition to the family. This study mainly investigated the novel marker IQGAP3 at serum and tumor tissue levels compared with the markers B7-H4 and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) and in healthy individuals, aiming to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic value of IQGAP3 for CRC.
Materials and methods: Serum samples were collected prior to any therapy in 118 CRC patients and as part of a routine examination in 85 healthy individuals. Serum IQGAP3, B7-H4 and COX-2 levels were measured using commercially available ELISA kits. Immunohistochemistry was performed to detect the IQGAP3, B7-H4 and COX-2 in tumor tissues and normal para-carcinoma tissues. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC) were used to evaluate and compare the diagnostic value of different serum tumor markers. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify the prognostic risk factors for CRC.
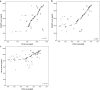
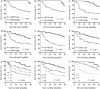
Results: IQGAP3, B7-H4 and COX-2 showed low or high expression in tumor tissues while no expression in normal para-carcinoma tissues. Serum levels of IQGAP3 in CRC group were significantly higher than those in healthy control group (P < 0.001). The IQGAP3 AUC was 0.799, while the B7-H4 AUC was 0.795 and the COX-2 AUC was 0.796. IQGAP3 seemed to be superior to B7-H4 and COX-2 in detecting CRC, with the highest sensitivity among the three markers. Multivariate analysis showed that T stage, N stage, differentiation degree, TNM stage and both serum and tissue IQGAP3, B7-H4 and COX-2 levels were significant prognostic factors for CRC.
Conclusions: IQGAP3 has a better diagnostic efficacy than B7-H4 and COX-2 in detecting CRC and it has value in predicting the prognosis of patients with CRC.
Keywords: B7-H4; Colorectal cancer; Cyclooxygenase-2; Diagnostic markers; IQ-motif-containing GTPase-activating protein; IQGAP3.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
B7-H4 is a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer and correlates with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.BMC Cancer. 2022 Oct 10;22(1):1053. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10159-5. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36217128 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Value of Combined Determination of Serum B7-H4 with Carcinoembryonic Antigen, Osteopontin, or Tissue Polypeptide-Specific Antigen for the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer.Dis Markers. 2018 Sep 27;2018:4310790. doi: 10.1155/2018/4310790. eCollection 2018. Dis Markers. 2018. PMID: 30363700 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of the IQ Motif-Containing GTPase-Activating Protein Family Indicates That the IQGAP3-PIK3C2B Axis Promotes Invasion in Colon Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Aug 20;13:8299-8311. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S257729. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32903879 Free PMC article.
-
The Antithetic Roles of IQGAP2 and IQGAP3 in Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;15(4):1115. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041115. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of IQ Motif-Containing GTPase-Activating Proteins in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 16;12:920652. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.920652. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IQGAP3 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma contributes to drug resistance and genome stability.PeerJ. 2022 Oct 18;10:e14201. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14201. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36275458 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Study on the Prognostic Value and Clinicopathological Significance of Different Immune Checkpoints in Patients With Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024 Sep 12;101:100760. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100760. eCollection 2024. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024. PMID: 39434898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Value of B7H4 Expression in Patients with Solid Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 6;25(9):5045. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095045. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732263 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the therapeutic potential of senescence-related IQGAP2 in pancreatic Cancer through post-GWAS genomic and scRNA-seq analyses.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 10;16(1):1301. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03078-x. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40640432 Free PMC article.
-
B7H4 Role in Solid Cancers: A Review of the Literature.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 11;16(14):2519. doi: 10.3390/cancers16142519. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, Andrews KS, Brooks D, Bond J, et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(5):1570–1595. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.002. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

