Extracellular vesicles carry cellulases in the industrial fungus Trichoderma reesei
- PMID: 31223336
- PMCID: PMC6570945
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-019-1487-7
Extracellular vesicles carry cellulases in the industrial fungus Trichoderma reesei
Abstract
Background: Trichoderma reesei is the most important industrial producer of lignocellulolytic enzymes. These enzymes play an important role in biomass degradation leading to novel applications of this fungus in the biotechnology industry, specifically biofuel production. The secretory pathway of fungi is responsible for transporting proteins addressed to different cellular locations involving some cellular endomembrane systems. Although protein secretion is an extremely efficient process in T. reesei, the mechanisms underlying protein secretion have remained largely uncharacterized in this organism.
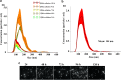
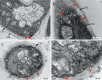
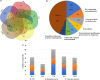
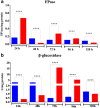
Results: Here, we report for the first time the isolation and characterization of T. reesei extracellular vesicles (EVs). Using proteomic analysis under cellulose culture condition, we have confidently identified 188 vesicular proteins belonging to different functional categories. Also, we characterized EVs production using transmission electron microscopy in combination with light scattering analysis. Biochemical assays revealed that T. reesei extracellular vesicles have an enrichment of filter paper (FPase) and β-glucosidase activities in purified vesicles from 24, 72 and 96, and 72 and 96 h, respectively. Furthermore, our results showed that there is a slight enrichment of small RNAs inside the vesicles after 96 h and 120 h, and presence of hsp proteins inside the vesicles purified from T. reesei grown in the presence of cellulose.
Conclusions: This work points to important insights into a better understanding of the cellular mechanisms underlying the regulation of cellulolytic enzyme secretion in this fungus.
Keywords: Cellulases; Extracellular vesicles; Proteome; Secretion; Trichoderma reesei.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into enzyme secretion by filamentous fungi: comparative proteome analysis of Trichoderma reesei grown on different carbon sources.J Proteomics. 2013 Aug 26;89:191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jun 21. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23796490
-
Penicillium janthinellum NCIM1366 shows improved biomass hydrolysis and a larger number of CAZymes with higher induction levels over Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2020 Dec 1;13(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01830-9. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2020. PMID: 33292411 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting Cellular Function and Distribution of β-Glucosidases in Trichoderma reesei.mBio. 2021 May 11;12(3):e03671-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03671-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33975944 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the molecular mechanisms behind cellulase production in Trichoderma reesei, the hyper-cellulolytic filamentous fungus.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2016 Sep;80(9):1712-29. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2016.1171701. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27075508 Review.
-
New Genomic Approaches to Enhance Biomass Degradation by the Industrial Fungus Trichoderma reesei.Int J Genomics. 2018 Sep 24;2018:1974151. doi: 10.1155/2018/1974151. eCollection 2018. Int J Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30345291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal Extracellular Vesicles Are Involved in Intraspecies Intracellular Communication.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0327221. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03272-21. Epub 2022 Jan 11. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35012355 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent roles of ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating proteins in lignocellulose utilization of Trichoderma guizhouense NJAU4742.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Sep 18;17(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02570-w. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 39294712 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Extracellular Vesicles in Interkingdom Communication.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2021;432:81-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-83391-6_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34972880
-
Analysis of Cryptococcal Extracellular Vesicles: Experimental Approaches for Studying Their Diversity Among Multiple Isolates, Kinetics of Production, Methods of Separation, and Detection in Cultures of Titan Cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0012521. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00125-21. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34346749 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Characterization, and Proteomic Analysis of Crude and Purified Extracellular Vesicles Extracted from Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;13(24):3534. doi: 10.3390/plants13243534. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adav SS, Sze SK. Trichoderma secretome: an overview. In: Gupta VK, Schmoll M, Herrera-Estrella A, Upadhyay RS, Druzhinina I, Tuohy MG, editors. Biotechnology and biology of Trichoderma. 1. Waltham: Elsevier; 2014. pp. 103–114.
-
- Samuels GJ. Trichoderma: a review of biology and systematics of the genus. Mycol Res. 1996;100:923–935. doi: 10.1016/S0953-7562(96)80043-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

