Discovery of Potent and Orally Bioavailable Inverse Agonists of the Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2
- PMID: 31223457
- PMCID: PMC6580541
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00158
Discovery of Potent and Orally Bioavailable Inverse Agonists of the Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2
Abstract
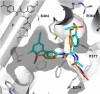
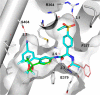
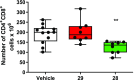
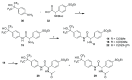
The further optimization of a recently disclosed series of inverse agonists of the nuclear receptor RORC2 is described. Investigations into the left-hand side of compound 1, guided by X-ray crystal structures, led to the substitution of the 4-aryl-thiophenyl residue with the hexafluoro-2-phenyl-propan-2-ol moiety. This change resulted in to compound 28, which combined improved drug-like properties with good cell potency and a significantly lower dose, using an early dose to man prediction. Target engagement in vivo was demonstrated in the thymus of mice by a reduction in the number of double positive T cells after oral dosing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Drug with Lipophilicity-Dependent Potency Can Be Metabolically Stable: Discovery of a Potent and Selective Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2 (RORC2) Inverse Agonist as an Orally Bioavailable Anti-Inflammatory Agent.J Med Chem. 2018 Dec 13;61(23):10412-10414. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01545. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30507131
-
Discovery of 3-Cyano- N-(3-(1-isobutyrylpiperidin-4-yl)-1-methyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-5-yl)benzamide: A Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2 Inverse Agonist.J Med Chem. 2018 Dec 13;61(23):10415-10439. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00392. Epub 2018 Sep 9. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30130103
-
AZD0284, a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Inverse Agonist of Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2.J Med Chem. 2021 Sep 23;64(18):13807-13829. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01197. Epub 2021 Aug 31. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34464130
-
Discovery of 1-{4-[3-fluoro-4-((3s,6r)-3-methyl-1,1-dioxo-6-phenyl-[1,2]thiazinan-2-ylmethyl)-phenyl]-piperazin-1-yl}-ethanone (GNE-3500): a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor C (RORc or RORγ) inverse agonist.J Med Chem. 2015 Jul 9;58(13):5308-22. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00597. Epub 2015 Jun 23. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26061388
-
Macrocyclic Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2 Inverse Agonists.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Jan 18;14(2):191-198. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00500. eCollection 2023 Feb 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 36793423 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
RORγt inverse agonists demonstrating a margin between inhibition of IL-17A and thymocyte apoptosis.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 16;20(1):e0317090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317090. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39820614 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical Analysis of Protein-Ligand Interaction Patterns in Nuclear Receptor RORγ.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 15;9:904445. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.904445. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35782874 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic ramoplanin analogues are accessible by effective incorporation of arylglycines in solid-phase peptide synthesis.Chem Sci. 2023 Sep 29;15(1):195-203. doi: 10.1039/d3sc01944f. eCollection 2023 Dec 20. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38131086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schnute M. E.; Wennerstål M.; Alley J.; Bengtsson M.; Blinn J. R.; Bolten C. W.; Braden T.; Bonn T.; Carlsson B.; Caspers N.; Chen M.; Choi C.; Collis L. P.; Crouse K.; Färnegårdh M.; Fennell K. F.; Fish S.; Flick A. C.; Goos-Nilsson A.; Gullberg H.; Harris P. K.; Heasley S. E.; Hegen M.; Hromockyj A. E.; Hu X.; Husman B.; Janosik T.; Jones P.; Kaila N.; Kallin E.; Kauppi B.; Kiefer J. R.; Knafels J.; Koehler K.; Kruger L.; Kurumbail R. G.; Kyne R. E.; Li W.; Löfstedt J.; Long S. A.; Menard C. A.; Mente S.; Messing D.; Meyers M. J.; Napierata L.; Nöteberg D.; Nuhant P.; Pelc M. J.; Prinsen M. J.; Rhönnstad P.; Backström-Rydin E.; Sandberg J.; Sandström M.; Shah F.; Sjöberg M.; Sundell A.; Taylor A. P.; Thorarensen A.; Trujillo J. I.; Trzupek J. D.; Unwalla R.; Vajdos F. F.; Weinberg R. A.; Wood D. C.; Xing L.; Zamaratski E.; Zapf C. W.; Zhao Y.; Wilhelmsson A.; Berstein G. Discovery of 3-Cyano-N-(3-(1-isobutyrylpiperidin-4-yl)-1-methyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)benzamide: A Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2 Inverse Agonist. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10415–10439. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00392. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sasaki Y.; Odan M.; Yamamoto S.; Kida S.; Ueyama A.; Shimizu M.; Haruna T.; Watanabe A.; Okuno T. Discovery of a potent orally bioavailable retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor-gamma-t (RORγt) inhibitor, S18–000003. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3549–3553. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.09.032. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ouvry G.; Bihl F.; Bouix-Peter C.; Christin O.; Defoin-Platel C.; Deret S.; Feret C.; Froude D.; Hacini-Rachinel F.; Harris C. S.; Hervouet C.; Lafitte G.; Luzy A.-P.; Musicki B.; Orfila D.; Parnet V.; Pascau C.; Pascau J.; Pierre R.; Raffin C.; Rossio P.; Spiesse D.; Taquet N.; Thoreau E.; Vatinel R.; Vial E.; Hennequin L. F. Sulfoximines as potent RORγ inverse agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1269–1273. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.03.041. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

