Prevalence of Hypertension and Associated Factors in Dire Dawa City, Eastern Ethiopia: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 31223500
- PMCID: PMC6541960
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9878437
Prevalence of Hypertension and Associated Factors in Dire Dawa City, Eastern Ethiopia: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a major cardiovascular risk factor that is linked with fatal complications and is an overwhelming global challenge. Primary prevention is a key to control hypertension with identification of major risk factors. This study was aimed at assessing the prevalence and factors associated with hypertension.
Methods: Community-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 903 adults aged 25 to 64 years in Dire Dawa City, East Ethiopia. Data were collected using World Health Organization (WHO) STEPwise approach to Surveillance (STEPS) for non-communicable disease (NCD) standard survey tool. Multivariate logistic regression models were used to identify relative effects of distal, proximal, and immediate risk factors of hypertension, and all statistical tests were declared significantly at P-value<0.05.
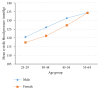
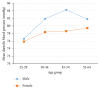
Results: The average SBP and DBP were 124.98±17.18 mmHg and 78.92±10.13 mmHg, respectively. The prevalence of hypertension was 24.43% (95% CI: 21.57, 27.28). Majority (51.64%) of adults were not aware of their elevated blood pressure status. hypertension was significantly associated with the age group 30-44 (aOR 3.61, 95% CI: 2.0, 6.55), 45-54 (aOR 5.36, 95% CI: 2.62, 10.91), and 55-64 (aOR 9.38, 95% CI: 4.73, 18.59), being unemployed (aOR 1.68, 95%CI: 1.03, 2.77), ever smoking (aOR 1.89, 95% CI: 1.04, 2.23), having abdominal obesity (aOR 1.72, 95% CI: 1.13, 2.64), and BMI≥25 kg/m2 (aOR 1.48, 95%CI: 1.01, 2.15).
Conclusion: Moderately high prevalence of hypertension was observed among adults in study setting demonstrating a major public health problem. Majority of adults with hypertension in study setting were not aware of their elevated BP status highlighting the burden of the hidden morbidity and subsequent complications. Community level intervention and routine assessment of sociodemographic, behavioral, and biophysiological risk factors, screening, and diagnosis of NCDs should be institutionalized to address the occult burden.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-care practices and associated factors among hypertension patients in public hospitals in Harari regional state and Dire Dawa City administration, Eastern Ethiopia: A multi-center cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 5;10:911593. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.911593. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35991019 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of pulmonary tuberculosis in public health facilities of Dire Dawa City, Eastern Ethiopia: Unmatched Case-control study.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2019 Apr-Jun;8(2):118-123. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_50_19. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31210152
-
Childhood overweight, obesity and associated factors among primary school children in dire dawa, eastern Ethiopia; a cross-sectional study.BMC Obes. 2017 Jun 1;4:20. doi: 10.1186/s40608-017-0156-2. eCollection 2017. BMC Obes. 2017. PMID: 28572983 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and associated factors of hypertension among adults in Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia: a community based cross-sectional study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2012 Nov 28;12:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-12-113. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2012. PMID: 23186560 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension among adults: A community based study in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 1;16(4):e0248934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248934. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33793641 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Magnitude of hypertension and its association with obesity among employees of Wallaga University, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2023 Jul 12;13(7):e070656. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070656. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37438078 Free PMC article.
-
Socio-demographic factors and health status of adults with disability in Enugu Metropolis, Nigeria.Malawi Med J. 2021 Mar;33(1):37-47. doi: 10.4314/mmj.v33i1.6. Malawi Med J. 2021. PMID: 34422232 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Hypertension and Associated Factors in Lubumbashi City, Democratic Republic of Congo: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Hypertens. 2021 Apr 7;2021:6674336. doi: 10.1155/2021/6674336. eCollection 2021. Int J Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 33880188 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of and risk factors for hypertension in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 22;4(3):e372. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.372. eCollection 2021 Sep. Health Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34589614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anemia among Adult Diabetic Patients Attending a General Hospital in Eastern Ethiopia: a Cross-sectional Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Feb 2;14:467-476. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S289298. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 33564253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kotcher T. Hypertensive Vascular Disease. 17. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies; 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources