Sortilin gates neurotensin and BDNF signaling to control peripheral neuropathic pain
- PMID: 31223654
- PMCID: PMC6584543
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aav9946
Sortilin gates neurotensin and BDNF signaling to control peripheral neuropathic pain
Abstract
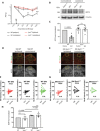
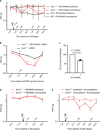
Neuropathic pain is a major incurable clinical problem resulting from peripheral nerve trauma or disease. A central mechanism is the reduced expression of the potassium chloride cotransporter 2 (KCC2) in dorsal horn neurons induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), causing neuronal disinhibition within spinal nociceptive pathways. Here, we demonstrate how neurotensin receptor 2 (NTSR2) signaling impairs BDNF-induced spinal KCC2 down-regulation, showing how these two pathways converge to control the abnormal sensory response following peripheral nerve injury. We establish how sortilin regulates this convergence by scavenging neurotensin from binding to NTSR2, thus modulating its inhibitory effect on BDNF-mediated mechanical allodynia. Using sortilin-deficient mice or receptor inhibition by antibodies or a small-molecule antagonist, we lastly demonstrate that we are able to fully block BDNF-induced pain and alleviate injury-induced neuropathic pain, validating sortilin as a clinically relevant target.
Figures



Similar articles
-
BDNF contributes to the development of neuropathic pain by induction of spinal long-term potentiation via SHP2 associated GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors activation in rats with spinal nerve ligation.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Jan;73:428-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.10.025. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25447233
-
BDNF Contributes to Spinal Long-Term Potentiation and Mechanical Hypersensitivity Via Fyn-Mediated Phosphorylation of NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit at Tyrosine 1472 in Rats Following Spinal Nerve Ligation.Neurochem Res. 2017 Oct;42(10):2712-2729. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2274-0. Epub 2017 May 11. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28497343
-
Down-regulation of zinc transporter-1 in astrocytes induces neuropathic pain via the brain-derived neurotrophic factor - K+-Cl- co-transporter-2 signaling pathway in the mouse spinal cord.Neurochem Int. 2016 Dec;101:120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27818163
-
The known knowns of microglia-neuronal signalling in neuropathic pain.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Dec 17;557 Pt A:37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.08.037. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23994389 Review.
-
Microglia in Neuropathic Pain.Adv Neurobiol. 2024;37:399-403. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-55529-9_22. Adv Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39207704 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysfunction of inhibitory interneurons contributes to synaptic plasticity via GABABR-pNR2B signaling in a chronic migraine rat model.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 May 26;16:1142072. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1142072. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37324588 Free PMC article.
-
An anti-sortilin affibody-peptide fusion inhibits sortilin-mediated progranulin degradation.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 8;15:1437886. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437886. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39185427 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Exercise on Neuropathic Pain in Preclinical Models: Perspectives for Neuroglia.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Mar;62(3):3684-3696. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04511-y. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39316356 Review.
-
Reduction of Pressure Pain Sensitivity as Novel Non-pharmacological Therapeutic Approach to Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Trial.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 11;15:613858. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.613858. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33776633 Free PMC article.
-
In Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, normalization of hemoglobin A1c accompanies reduced sensitivity to pressure at the sternum.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 14;17:1067098. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1067098. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37389368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Hecke O., Austin S. K., Khan R. A., Smith B. H., Torrance N., Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 155, 654–662 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Coull J. A. M., Boudreau D., Bachand K., Prescott S. A., Nault F., Sík A., De Koninck P., De Koninck Y., Trans-synaptic shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism of neuropathic pain. Nature 424, 938–942 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Doyon N., Vinay L., Prescott S. A., De Koninck Y., Chloride regulation: A dynamic equilibrium crucial for synaptic inhibition. Neuron 89, 1157–1172 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Coull J. A. M., Beggs S., Boudreau D., Boivin D., Tsuda M., Inoue K., Gravel C., Salter M. W., De Koninck Y., BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 438, 1017–1021 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

