Biology and clinical relevance of EpCAM
- PMID: 31225512
- PMCID: PMC6558934
- DOI: 10.15698/cst2019.06.188
Biology and clinical relevance of EpCAM
Abstract
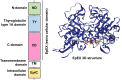
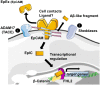
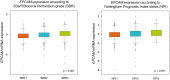
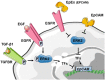
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily known to mediate homotypic cell contacts in epithelia tissues. Because EpCAM expression is limited to normal and malignant epithelia, it has been used as diagnostic marker for the detection of carcinoma cells in mesenchymal organs such as blood, bone marrow or lymph nodes. In particular, the detection and molecular characterization of EpCAM-positive circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the blood of carcinoma patients has gained considerable interest over the past ten years. EpCAM is primarily considered as an adhesion molecule, but recent studies have shown diverse biological functions including regulation of cell proliferation and cancer stemness. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the biological properties of EpCAM with emphasis on mechanisms involved in cancer progression and discuss the clinical implications of these findings for the clinical use of EpCAM as a diagnostic marker.
Keywords: EMT; EpCAM; Tumor biomarker; circulating tumor cells; liquid biopsy; tumor cell dissemination.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: K.P. has ongoing patent applications related to circulating tumor cells. K.P. has received honoraria from Agena, Novartis, Roche and Sanofi and research funding from European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) partners (Angle, Menarini and Servier) of the CANCER-ID programme of the European Union–EFPIA Innovative Medicines Initiative. L.K and S.W. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
