Nucleic Acid Detection of Plant Genes Using CRISPR-Cas13
- PMID: 31225754
- PMCID: PMC7001462
- DOI: 10.1089/crispr.2019.0011
Nucleic Acid Detection of Plant Genes Using CRISPR-Cas13
Abstract
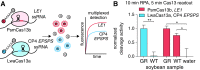
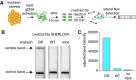
Nucleic acid detection is vital for agricultural applications including trait detection during breeding, pest surveillance, and pathogen identification. Here, we use a modified version of the CRISPR-based nucleic acid detection platform SHERLOCK to quantify levels of a glyphosate resistance gene in a mixture of soybeans and to detect multiple plant genes in a single reaction. SHERLOCK is rapid (∼15 min), quantitative, and portable, and can process crude soybean extracts as input material for minimal nucleic acid sample preparation. This field-ready SHERLOCK platform with color-based lateral flow readout can be applied for detection and quantitation of genes in a range of agricultural applications.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S.G., O.O.A, M.J.K., and F.Z. are co-inventors on patent applications filed by the Broad Institute relating to work in this study. J.S.G., O.O.A., and F.Z. are co-founders of Sherlock Biosciences. F.Z. is a co-founder and advisor of Beam Therapeutics, Editas Medicine, Pairwise Plants, and Arbor Biotechnologies. O.O.A. and J.S.G. are advisors for Beam Therapeutics. J.S.G. is a campus advisor of Benchling, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Oerke EC. Crop losses to pests. J Agric Sci 2006;144:31–43. DOI: 10.1017/S0021859605005708 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

