Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus-based treatment for nephrotic idiopathic membranous nephropathy in young adults: A retrospective study
- PMID: 31225949
- PMCID: PMC11900774
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12098
Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus-based treatment for nephrotic idiopathic membranous nephropathy in young adults: A retrospective study
Abstract
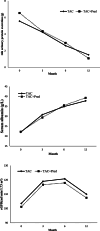
In China, the prevalence of idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN) is increasing with a younger age of onset. From January 2012 to October 2018, biopsy-proven nephrotic IMN patients aged between 15 and 40 in Taian City Central Hospital treated with tacrolimus (TAC) were retrospectively analyzed. Twelve-month follow-up data were collected. A total of 86 patients were enrolled in this study. Forty patients in the TAC group received TAC monotherapy with an initial dose of 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg/day. Forty-six patients in the TAC + Pred group received TAC combined with oral prednisone (0.5 mg/kg/day initially). Remission rate, relapse rate, and adverse events in the two groups were assessed. Total remission (TR) rates at the end of the 3rd, 6th, and 12th month were 15%, 35%, and 77.5% (TAC group) and 28.3%, 56.5%, and 80.4% (TAC + Pred group), respectively. Compared with the TAC group, the TAC + Pred group had higher complete remission rates at the end of the 6th and 12th month, and TR rate at the 6th month was significantly higher. Twenty-four-hour urinary protein excretion, serum albumin and estimated glomerular filtration rate between the two groups were comparable during the follow-up. Decrease in proteinuria was significantly greater in the TAC + Pred group. No significant difference of relapse rate was found between the two groups. Adverse effects in the two groups were mild and controllable. Both TAC monotherapy and TAC combined with medium-dose prednisone are effective and safe for young adults with nephrotic IMN, while TAC + Pred regimen brings more benefits.
Keywords: Tacrolimus; nephrotic IMN; prednisone; young adults.
© 2019 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Massry SG, Glassock RJ. Massry & Glassock's textbook of nephrology. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001;p. 701–713.
-
- Du Buf‐Vereijken PW, Branten AJ, Wetzels JF. Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: Outline and rationale of a treatment strategy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;46(6):1012–1029. - PubMed
-
- Schieppati A, Mosconi L, Perna A, Mecca G, Bertani T, Garattini S, et al. Prognosis of untreated patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:85–89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources