Mucosal Injury during Anti-Cancer Treatment: From Pathobiology to Bedside
- PMID: 31226812
- PMCID: PMC6627284
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11060857
Mucosal Injury during Anti-Cancer Treatment: From Pathobiology to Bedside
Abstract
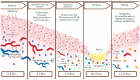
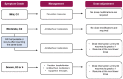
Mucositis is one of the most common debilitating side effects related to chemotherapy (CT), radiation therapy (RT), targeted agents and immunotherapy. It is a complex process potentially involving any portion of the gastrointestinal tract and injuring the mucosa, leading to inflammatory or ulcerative lesions. Mechanisms and clinical presentation can differ according both to the anatomic site involved (oral or gastrointestinal) and the treatment received. Understanding the pathophysiology and management of mucosal injury as a secondary effect of anti-cancer treatment is an important area of clinical research. Prophylaxis, early diagnosis, and adequate management of complications are essential to increase therapeutic success and, thus, improve the survival outcomes of cancer patients. This review focuses on the pathobiology and management guidelines for mucositis, a secondary effect of old and new anti-cancer treatments, highlighting recent advances in prevention and discussing future research options.
Keywords: anti-cancer treatments; mucosal impairment; mucosal injury; mucositis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pico J.-L., Avila-Garavito A., Naccache P. Mucositis: Its occurrence, consequences, and treatment in the oncology setting. Oncologist. 1998;3:446–451. - PubMed
-
- Bensinger W., Schubert M., Ang K.K., Brizel D., Brown E., Eilers J.G., Elting L., Mittal B.B., Schattner M.A., Speilberg R., et al. NCCN Task Force Report—Prevention and management of mucositis in cancer care. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2008;6:S1–S21. - PubMed
-
- Sonis S.T., Elting L.S., Keefe D., Peterson D.E., Schubert M., Hauer-Jensen M., Bekele B.N., Raber-Durlacher J., Donnelly J.P., Rubenstein E.B., et al. Perspectives on cancer therapy-induced mucosal injury: Pathogenesis, measurement, epidemiology, and consequences for patients. Cancer. 2004;100:1995–2025. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20162. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mortensen H.R., Overgaard J., Specht L., Overgaard M., Johansen J., Evensen J.F., Andersen L.J., Andersen E., Grau C. Prevalence and peak incidence of acute and late normal tissue morbidity in the DAHANCA 6&7 randomised trial with accelerated radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2012;103:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Blijlevens N., Schwenkglenks M., Bacon P., D’Addio A., Einsele H., Maertens J., Niederwieser D., Rabitsch W., Roosaar A., Ruutu T., et al. Prospective oral mucositis audit: Oral mucositis in patients receiving high-dose melphalan or BEAM conditioning chemotherapy--European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Mucositis Advisory Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:1519–1525. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.6028. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

